Figure 2.
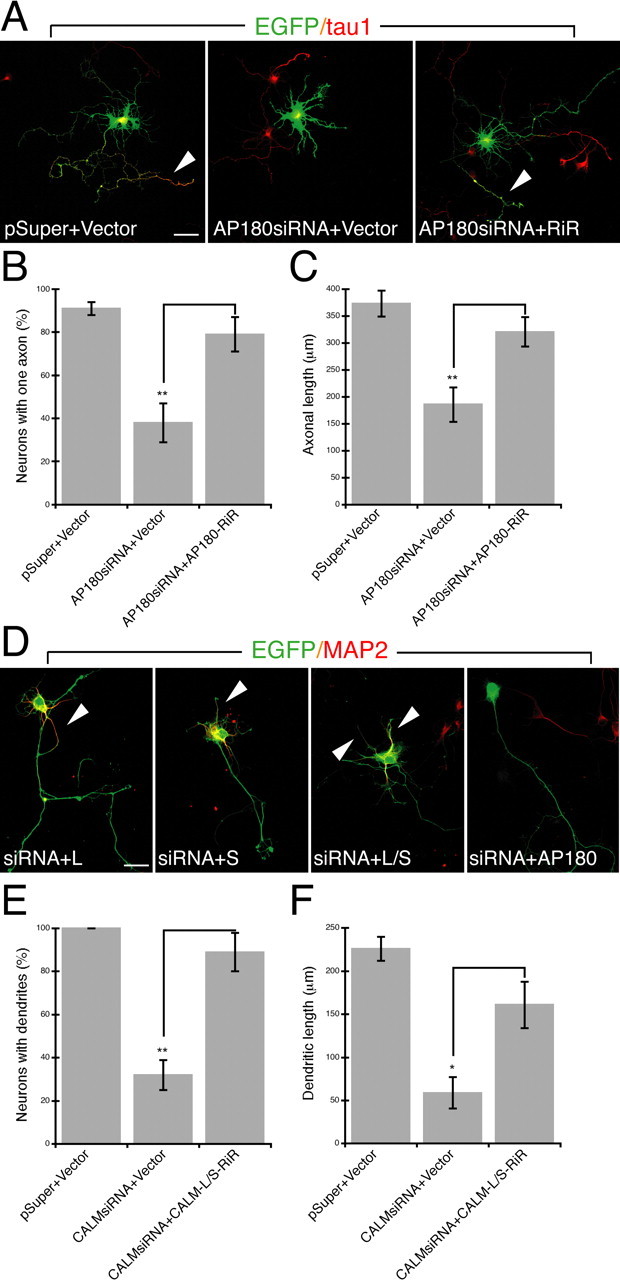
A–F, The effect of siRNA can be rescued by the expression of siRNA-resistant construct. A, Immunolabeling of the axonal marker tau1 (red) in neurons coexpressing EGFP (green), the siRNA, and siRNA-resistant AP180 (AP180-RiR). Shown are merged confocal images. pSuper, the vector for the siRNA; Vector, the vector for AP180-RiR. Arrowheads indicate the axon. Scale bar, 10 μm. B, Quantification of neurons with one axon. n = 45 neurons in each group. Comparison is no rescue (AP180siRNA+Vector) versus rescue (AP180siRNA+AP180-RiR), **p < 0.001. C, The mean length of axons. n = 20–30 neurons. Comparison is no rescue versus rescue, **p < 0.001. D, Immunolabeling of the dendritic marker MAP2 (red) in neurons coexpressing EGFP (green), the siRNA, and siRNA-resistant CALM (CALM-RiR). Arrowheads indicate dendrites. Scale bar, 10 μm. E, Quantification of neurons containing MAP2-labeled dendrites. n = 45 neurons in each group. Comparison is no rescue (CALMsiRNA+Vector) versus rescue (CALMsiRNA+CALM-L-RiR+CALM-S-RiR), **p < 0.001. F, The total length of dendrites. n = 15–30 neurons. Comparison is no rescue versus rescue, *p < 0.01. Data represent means ± SEM in B, C, E, F.
