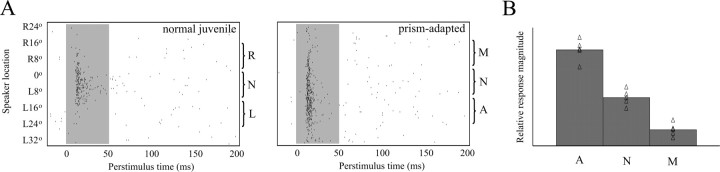
Figure 2.
Electrophysiological mapping. A, Top, Representative raster plot showing auditory tuning in a normal juvenile. The shaded region indicates duration of sound stimulus. Sound-evoked action potentials are represented as ticks. The visual receptive field at this site was centered at L4°, which predicts range of normal auditory responses (N). Bottom, Representative raster plot from an owl adapted to R19° prisms. R-shifting prisms require the acquisition of L-ear leading responses. The visual receptive field for this site was centered at L3°. The predicted normal (N) and maladaptive (M) auditory responses are weak, whereas the predicted adaptive responses (A) are strong. B, Summary data from five prism-adapted owls that were subsequently analyzed for contact clustering. The triangles represent the relative response magnitudes in each zone for each animal, and the bars indicate the mean across animals.