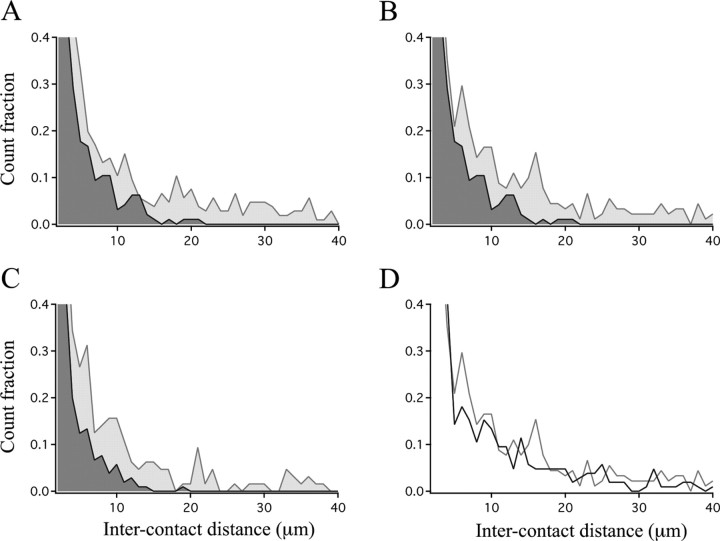
Figure 8.
Frequency histograms of ICDs across adaptive, normal, and maladaptive zones. Frequency distributions of ICDs for each zone were normalized to peak, which occurred in the first bin (ICD, 2–3 μm) for all zones. A, Light gray, Maladaptive zone of prism owls; dark gray, adaptive zone of prism owls (n = 426 and 258 ICDs, respectively; p < 0.0001). B, Light gray, Right space zone of normal juveniles; dark gray, adaptive zone of prism owls (n = 485 and 258 ICDs, respectively; p < 0.0001). C, Light gray, Normal zone of prism owls; dark gray, normal zone of normal juveniles (n = 261 and 235 ICDs, respectively; p < 0.0001). D, Light gray line, Maladaptive zone of prism owls; black line, left space zone of normal juveniles (n = 426 and 418 ICDs, respectively; p < 0.0176). The p values were determined by the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test.