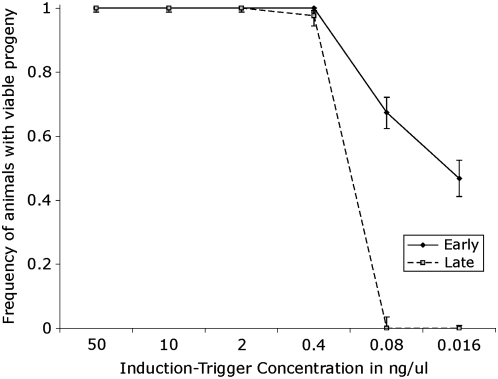
Figure 5.—
Comparison of silencing efficiency between early and late-born progeny. We injected animals and selected F1 progeny by birth order and determined their silencing capacity. We segregated animals from the same brood as (1) early born animals (born the first 24 hr after the injection) and (2) late-born animals (born the second 24 hr after injection). We found injected concentrations of 50, 10, 2, and 0.4 ng/μl show no significant difference in silencing between early and late-born siblings. In contrast, at concentrations of 0.08 and 0.016 ng/μl, there is a significant difference between the early born animals (solid line) and late-born animals (dashed line). Early born progeny of injection concentrations of 0.08 and 0.016 ng/μl had silencing frequencies of 67.4 and 46.7%, respectively, while the late-born progeny for both concentrations has a silencing frequency of 0%. Bars represent 1 SD.