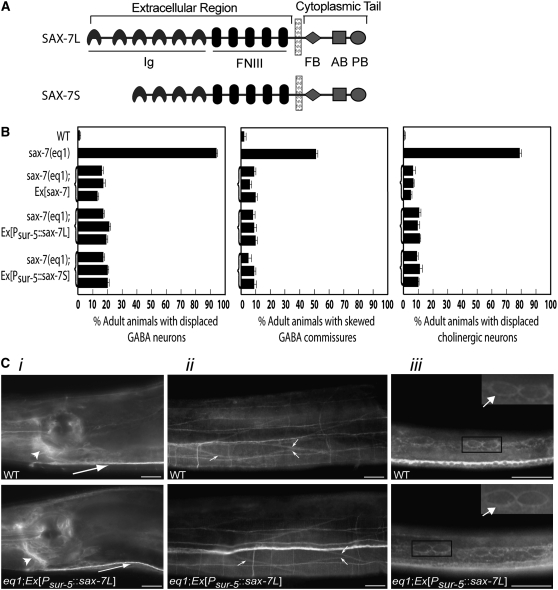
Figure 2.—
Psur-5∷sax-7 is similarly expressed as endogenous sax-7 in wild-type animals and rescues the positional defects in the GABA neuronal soma and commissural axons in sax-7(eq1) animals just as well as genomic sax-7 does. (A) A schematic of the two SAX-7 protein isoforms, SAX-7L and SAX-7S. The extracellular region contains immunoglobulin (Ig) and fibronectin type III (FNIII) repeats while the cytoplasmic tail contains the FB, AB, and PB motifs. (B) Quantitation of displaced cholinergic and GABA neurons and commissural axons in wild-type, sax-7(eq1), and transgenic sax-7(eq1) animals. Three independent transgenic lines for each construct were analyzed. Error bar shows standard error of the proportions of three sample sets where in each set n = 100. (C) Immunofluorescence analyses of transgenic sax-7(eq1) animals show that transgenic SAX-7 is similarly expressed and localized as endogenous SAX-7 in wild-type animals in multiple tissues, including the nervous system (i), body-wall muscle (ii), and hypodermis (iii), the three tissues where sax-7 activity is required for optimal positioning maintenance of GABA neurons. Respective images of wild-type and transgenic sax-7(eq1) animals are taken with the same exposure times. SAX-7 is present in (i) the nerve ring (large arrow) and ventral nerve cord (small arrow), (ii) the cell membrane of the elliptical-shaped body-wall muscle cells (arrows), and (iii) the cell membrane of the hypodermal seam cells (the arrows in the enlarged insets show SAX-7 localization on the membrane of two seam cells). Bar, 20 μm.