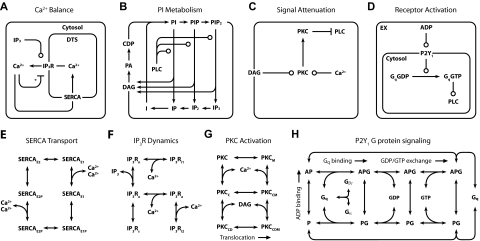
Figure 2.
Detailed reaction schemes for platelet signaling modules. (A) Ca2+ module: cytosolic and DTS compartments are separated by the DTS membrane, which contains the IP3R and SERCA. (B) PI module: PM-bound PIs are cleaved by PLC-β to form diffusible inositol phosphates and DAG, which are substrates for resynthesis of PIs. (C) PKC module: Ca2+i and DAG activate PKC, which migrates to the PM where it phosphorylates PLC-β. (D) P2Y1 module: extracellular ADP binds to and activates P2Y1. Active P2Y1 accelerates guanine nucleotide exchange on bound Gq. Gq-GTP binds and activates PLC-β, which increases the GTPase activity of Gq-GTP. (E) SERCA catalytic cycle24: Subscripts: E1, facing cytosol; E2, facing DTS; P, phosphorylated. (F) IP3R dynamics25: Subscripts: n, native; i1, inhibited; o, open; a, active; s, shut, i2, inhibited. (G) PKC activation: Active kinase is bound to Ca2+i and DAG and located at the PM. Subscripts: M, located at the PM; C, Ca2+-bound; D, DAG-bound. (H) P2Y1 activation module: Rate equations describing the interactions among ADP, P2Y1, and Gq were modeled according to the ternary complex model described by Kinzer-Ursem et al46 For clarity, DTS membrane and cytosolic compartments are not delineated. A indicates ADP; P, P2Y1; G, Gq. *Ca2+ both activates and inhibits IP3R.25