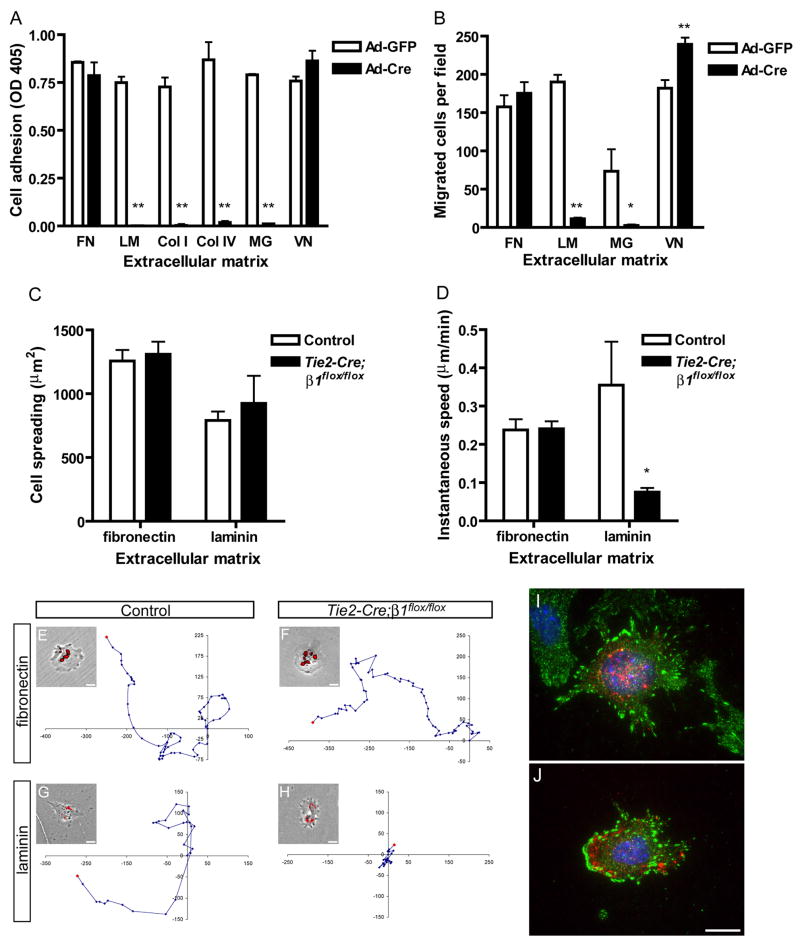
Figure 6. β1 integrins are required for EC adhesion and migration in a matrix-specific manner.
Analysis of immortalized embryonic β1flox/flox ECs (A, B) or primary embryonic ECs (C–J). (A) Adhesion of adenovirus (Ad) infected embryonic β1flox/flox ECs in serum-free medium after 30 min. Microplate coating concentrations were: fibronectin (FN), 20 nM; laminin (LM), 25 nM; collagen I (Col I), 55 nM; collagen IV (Col IV), 40 nM; Matrigel (MG), 125 μg/ml; vitronectin (VN), 20 nM. (B) Haptotactic migration of embryonic β1flox/flox ECs in serum-free medium after 4 hr. The ECM that served as the stimulus for migration was coated to the underside of a filter at the following concentrations: FN, 40 nM; LM, 50 nM; MG, 500 μg/ml; VN, 20 nM. (C) Cell spreading after 20 hr culture. (D) Migration speed measured over 24 hr (fibronectin) or 14 hr (laminin) by timelapse videomicroscopy. (E–H) Representative migration tracks along with a phase contrast image overlaid with DiI-Ac-LDL uptake fluorescence. Units on migration tracks are pixels. Coating concentrations were: fibronectin, 40 nM; laminin, 15 nM. Focal adhesion formation in control (I) and mutant (J) embryonic ECs on fibronectin as assessed by anti-FAKpY397 (green), anti-CD31 (red), and DAPI (blue) staining. Values in panels A and B are means + SD, and in panels C and D are means + SEM. **p < 0.01 and *p < 0.05 by Student’s T-test. All experiments were performed at least twice and representative results are shown. Bars, 20 μm.