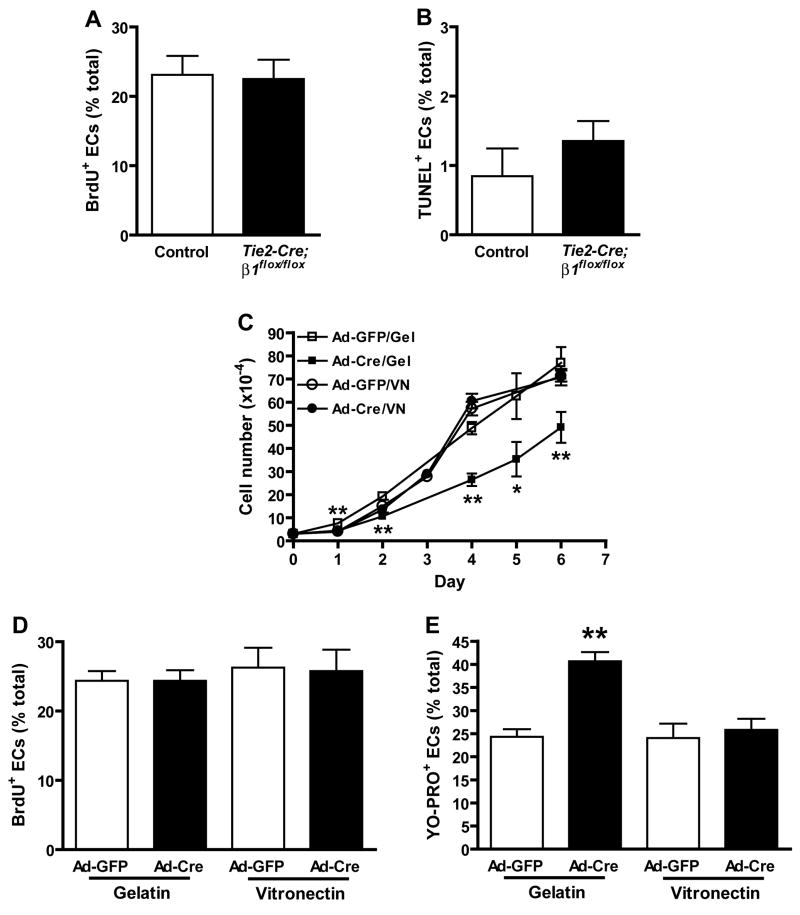
Figure 7. β1 integrins regulate EC growth through effects on survival rather than proliferation.
In vivo (A, B) and in vitro (C–E) effects of β1 deletion on EC growth. The ratios of BrdU/CD31 (A) and TUNEL/CD31 (B) double positive ECs relative to total ECs were calculated from multiple immunostained cryosections prepared from 3 (A) or 4 (B) pairs of control and Tie2-Cre mutant embryos at e9.0 prior to the onset of overt morbidity. Bars in panels A and B are means + SEM, and differences are not statistically significant by Student’s T-test (A, n = 1200 control and 965 Tie2-Cre mutant EC, p = 0.625; B, n = 1299 control and 1116 mutant EC, p = 0.36). (C) Growth rate of embryonic β1flox/flox ECs cultured on gelatin (Gel) or vitronectin (VN). (D) Incorporation of BrdU into DNA after 6 hr culture. (E) Entry of the apoptotic cell permeant dye, YO-PRO-1, into proliferating EC cultures. Panel C-E data are means + SD of replicate measurements, and each experiment was repeated with similar results. *p < 0.01 and *p < 0.05 by Student’s T-test.