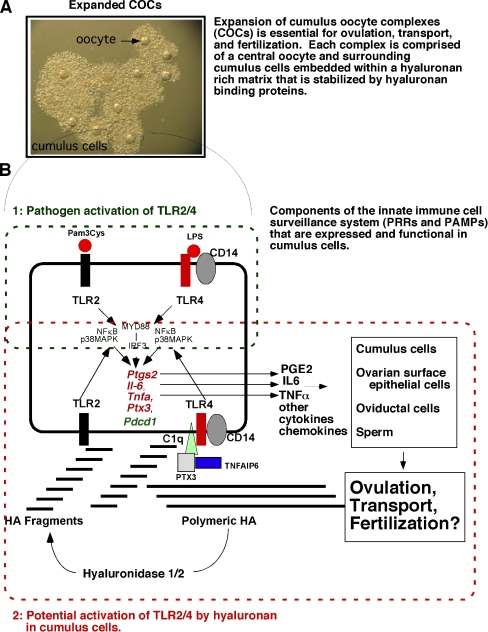
Fig. 1.
Schematic of TLR pathway activation and functions in cumulus cells during COC expansion, ovulation, transport and fertilization. A In response to the ovulatory surge of LH, cumulus cell-oocyte complexes (COCs) undergo expansion. This process requires the synthesis of a hyaluronan (HA)-rich matrix and factors that bind HA to stabilize the matrix. This process is critical for ovulation. B Cumulus cells express members of the Toll-like receptor (TLR) superfamily and can respond to specific ligands (1: pathogen-derived or 2: matrix-derived) leading to the induction of inflammation- and innate immune-related genes. These include: Ptgs2, Il6, Tnfaip6, Tnfa and Pdcd1. Prostaglandins (PGE2) synthesized by PTGS2, IL6, TNFa as well as other cytokines and chemokines are released from cumulus cells and can impact the function not only of the cumulus cells but also oviductal cells during transport and sperm during fertilization. The degradation of polymeric HA by hyaluronidases is presumed to lead to the generation of HA fragments that activate TLR2 and TLR4