Abstract
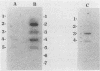
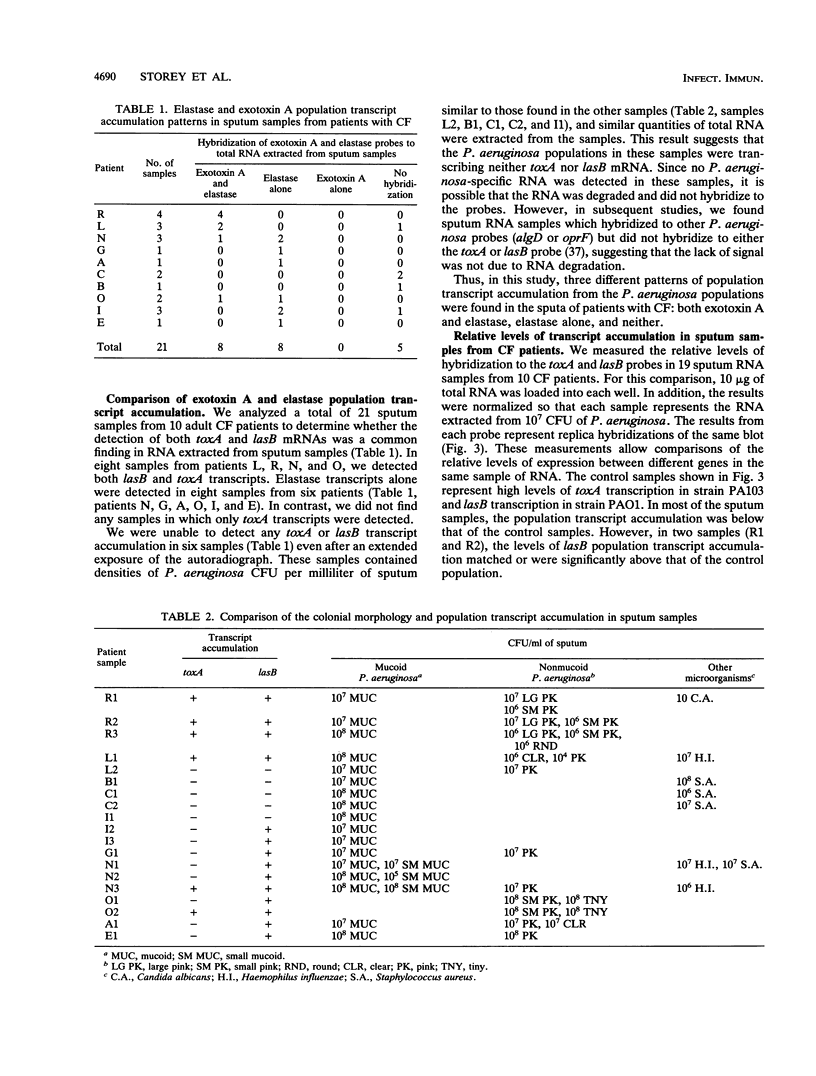
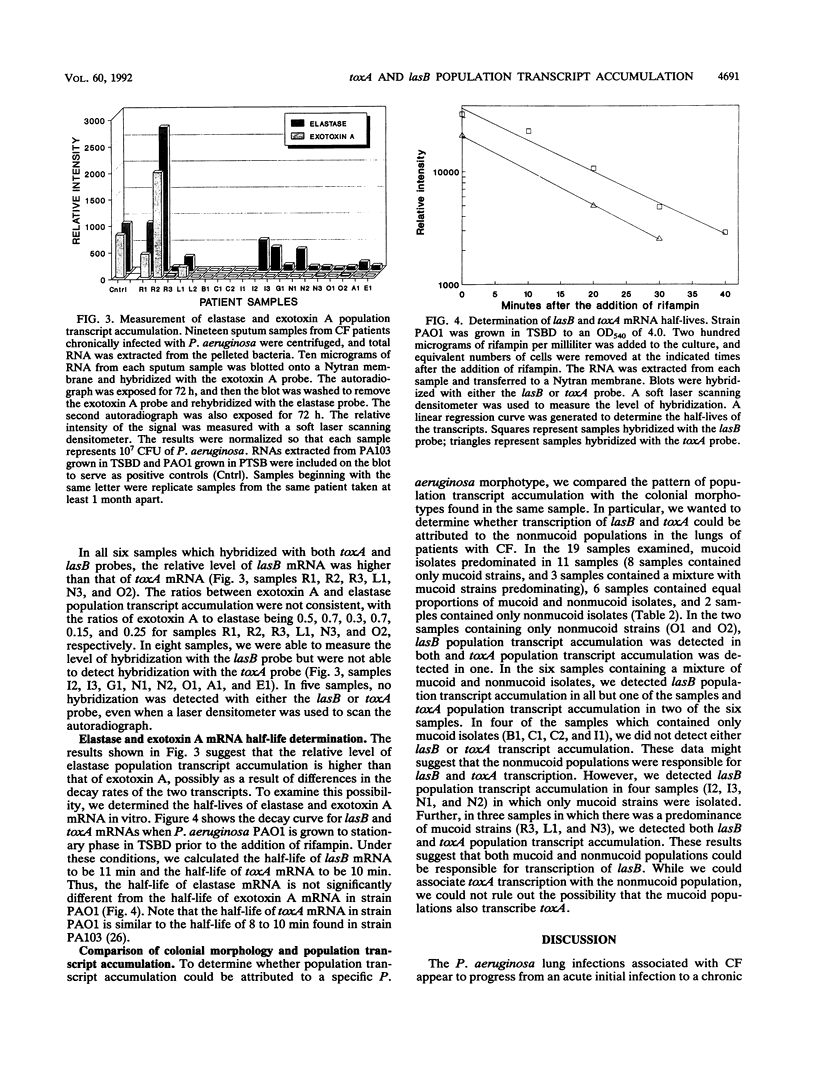
The in vivo regulation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factors during the chronic lung infections associated with cystic fibrosis is poorly understood. We have developed an approach for the analysis of transcript accumulation of individual virulence factors from the P. aeruginosa populations found in the sputa of patients with cystic fibrosis. This method has been named population transcript accumulation, since we examine the transcript accumulation patterns in RNA extracted from the total bacterial population found in the sputum samples. DNA probes specific for P. aeruginosa elastase (lasB) and exotoxin A (toxA) were used to examine the population transcript accumulation of 21 sputum samples taken from 10 patients. We detected three patterns of population transcript accumulation: lasB and toxA, lasB alone, and neither lasB nor toxA. We also measured the relative levels of elastase and exotoxin A transcript accumulation in 19 of these samples. In the six samples containing both toxA and lasB transcripts, we found that the levels of lasB transcripts were consistently higher than those of toxA. Differences in the stability of the two mRNA species could not completely account for the higher level of lasB population transcript accumulation, since we showed that the mRNA half-life of lasB (11 min) was similar to that of toxA (10 min). Finally, we showed that elastase transcripts could be detected in some samples which contained only mucoid isolates. This finding suggests that both mucoid and nonmucoid populations may be transcribing lasB in the lungs of patients with cystic fibrosis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bainbridge T., Fick R. B., Jr Functional importance of cystic fibrosis immunoglobulin G fragments generated by Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase. J Lab Clin Med. 1989 Dec;114(6):728–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bever R. A., Iglewski B. H. Molecular characterization and nucleotide sequence of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase structural gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4309–4314. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4309-4314.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cukor G., Blacklow N. R., Nowak N. A., Rich C. M., Braverman L. E., Fischer R. A. Comparative analysis of serum antibody responses to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A by cystic fibrosis and intensive care unit patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):457–462. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.457-462.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DI SANT'AGNESE P. A., DARLING R. C., PERERA G. A., SHEA E. Sweat electrolyte disturbances associated with childhood pancreatic disease. Am J Med. 1953 Dec;15(6):777–784. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(53)90169-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOGGETT R. G., HARRISON G. M., WALLIS E. S. COMPARISON OF SOME PROPERTIES OF PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA ISOLATED FROM INFECTIONS IN PERSONS WITH AND WITHOUT CYSTIC FIBROSIS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Feb;87:427–431. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.2.427-431.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doggett R. G. Incidence of mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa from clinical sources. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):936–937. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.936-937.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döring G., Buhl V., Høiby N., Schiøtz P. O., Botzenhart K. Detection of proteases of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in immune complexes isolated from sputum of cystic fibrosis patients. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1984 Oct;92(5):307–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1984.tb00092.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döring G., Goldstein W., Röll A., Schiøtz P. O., Høiby N., Botzenhart K. Role of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzymes in lung infections of patients with cystic fibrosis. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):557–562. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.557-562.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döring G., Høiby N. Longitudinal study of immune response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa antigens in cystic fibrosis. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):197–201. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.197-201.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esterly J. R., Oppenheimer E. H. Cystic fibrosis of the pancreas: structural changes in peripheral airways. Thorax. 1968 Nov;23(6):670–675. doi: 10.1136/thx.23.6.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fick R. B., Jr Pathogenesis of the pseudomonas lung lesion in cystic fibrosis. Chest. 1989 Jul;96(1):158–164. doi: 10.1378/chest.96.1.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank D. W., Iglewski B. H. Kinetics of toxA and regA mRNA accumulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4477–4483. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4477-4483.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank D. W., Storey D. G., Hindahl M. S., Iglewski B. H. Differential regulation by iron of regA and toxA transcript accumulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5304–5313. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5304-5313.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilligan P. H. Microbiology of airway disease in patients with cystic fibrosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jan;4(1):35–51. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R., Harris G. S. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and cystic fibrosis: unusual bacterial adaptation and pathogenesis. Microbiol Sci. 1986 Oct;3(10):302–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granström M., Ericsson A., Strandvik B., Wretlind B., Pavlovskis O. R., Berka R., Vasil M. L. Relation between antibody response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoproteins and colonization/infection in patients with cystic fibrosis. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1984 Nov;73(6):772–777. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1984.tb17774.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holby N., Olling S. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis. Bactericidal effect of serum from normal individuals and patients with cystic fibrosis on P. aeruginosa strains from patients with cystic fibrosis or other diseases. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1977 Apr;85(2):107–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollsing A. E., Granström M., Vasil M. L., Wretlind B., Strandvik B. Prospective study of serum antibodies to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoproteins in cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1868–1874. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1868-1874.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagger K. S., Bahner D. R., Warren R. L. Protease phenotypes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):55–59. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.55-59.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagger K. S., Robinson D. L., Franz M. N., Warren R. L. Detection by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays of antibody specific for Pseudomonas proteases and exotoxin A in sera from cystic fibrosis patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1054–1058. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1054-1058.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinger J. D., Straus D. C., Hilton C. B., Bass J. A. Antibodies to proteases and exotoxin A of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis: Demonstration by radioimmunoassay. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jul;138(1):49–48. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles M., Gatzy J., Boucher R. Relative ion permeability of normal and cystic fibrosis nasal epithelium. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1410–1417. doi: 10.1172/JCI110894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lory S. Effect of iron on accumulation of exotoxin A-specific mRNA in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1451–1456. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1451-1456.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May T. B., Shinabarger D., Maharaj R., Kato J., Chu L., DeVault J. D., Roychoudhury S., Zielinski N. A., Berry A., Rothmel R. K. Alginate synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a key pathogenic factor in chronic pulmonary infections of cystic fibrosis patients. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Apr;4(2):191–206. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.2.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss R. B., Hsu Y. P., Lewiston N. J., Curd J. G., Milgrom H., Hart S., Dyer B., Larrick J. W. Association of systemic immune complexes, complement activation, and antibodies to Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide and exotoxin A with mortality in cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Apr;133(4):648–652. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.4.648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman D. E., Chakrabarty A. M. Utilization of human respiratory secretions by mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa of cystic fibrosis origin. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):662–669. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.662-669.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman D. E., Sadoff J. C., Iglewski B. H. Toxin A-deficient mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA103: isolation and characterization. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):899–908. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.899-908.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penketh A., Pitt T., Roberts D., Hodson M. E., Batten J. C. The relationship of phenotype changes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the clinical condition of patients with cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 May;127(5):605–608. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.5.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B. Pulmonary disease associated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis: current status of the host-bacterium interaction. J Infect Dis. 1985 Apr;151(4):575–580. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.4.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Callahan L. T., 3rd, Taylor N. S. Neutralizing antibody to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin in human sera: evidence for in vivo toxin production during infection. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):942–947. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.942-947.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schad P. A., Bever R. A., Nicas T. I., Leduc F., Hanne L. F., Iglewski B. H. Cloning and characterization of elastase genes from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2691–2696. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2691-2696.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobonya R. E., Taussig L. M. Quantitative aspects of lung pathology in cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Aug;134(2):290–295. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.2.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutman H. R., Marks M. I. Pulmonary infections in children with cystic fibrosis. Semin Respir Infect. 1987 Sep;2(3):166–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomassen M. J., Demko C. A., Doershuk C. F. Cystic fibrosis: a review of pulmonary infections and interventions. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1987 Sep-Oct;3(5):334–351. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950030510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch D. F., Muszynski M. J., Pai C. H., Marcon M. J., Hribar M. M., Gilligan P. H., Matsen J. M., Ahlin P. A., Hilman B. C., Chartrand S. A. Selective and differential medium for recovery of Pseudomonas cepacia from the respiratory tracts of patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1730–1734. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1730-1734.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilmott R. W., Tyson S. L., Matthew D. J. Cystic fibrosis survival rates. The influences of allergy and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Am J Dis Child. 1985 Jul;139(7):669–671. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1985.02140090031019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. E., Boat T. F., Doershuk C. F. Cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Jun;113(6):833–878. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.6.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Schaffer M. S., Rabin H. R., Campbell G. D., Sokol P. A. Phenotypic comparison of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from a variety of clinical sites. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Aug;24(2):260–264. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.2.260-264.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Sokol P. A., Bryan L. E., Storey D. G., Mattingly S. J., Vogel H. J., Ceri H. In vivo regulation of virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa associated with genetic rearrangement. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jan;163(1):143–149. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.1.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., To M., Sokol P. A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S as a pathogenic determinant in respiratory infections. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1989;42:27–35. doi: 10.1159/000417600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]