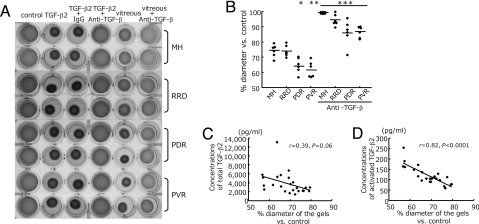
Fig. 2.
Role of TGF-β in vitreous-induced collagen gel contraction. (A) Hyalocyte-containing collagen gels were exposed to control (DMEM), recombinant TGF-β2 (0.3 nM), or patient vitreous, with anti-TGF-β mAb (10 ng/ml) or control IgG (10 ng/ml) (n = 6 in each group). Two representative wells per condition, 3 days after stimulation, are shown. (B) The diameters of the gels treated with vitreous (lane 5 in A and vitreous with anti-TGF-β mAb lane 6 in A were measured and expressed as a percentage of the diameter of control (lane 1 in A). *, P = 0.01 vs. MH and P = 0.007 vs. RRD; **, P = 0.007 vs. MH and P = 0.004 vs. RRD; ***, P < 0.0001 vs. each disease without anti-TGF-β mAb. (C and D) The correlation of the diameters of the gels with concentration of total TGF-β2 in the vitreous (n = 24, r = 0.39, P = 0.06) (C) and with activated TGF-β2 (n = 24, r = 0.82, P < 0.0001) (D).