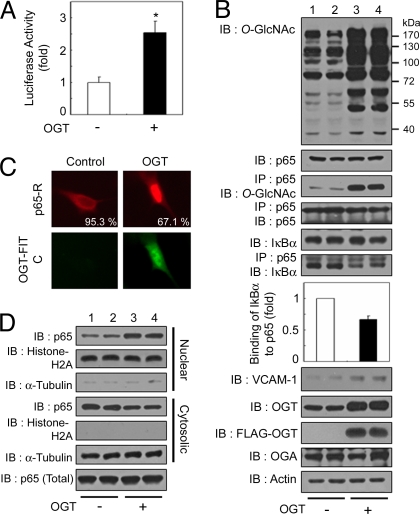
Fig. 3.
OGT overexpression-mediated increase in O-GlcNAcylation induces the up-regulation of NFκB activity. (A) VSMCs were transfected with the κB-luciferase reporter gene plasmid and the plasmid encoding FLAG-tagged OGT and incubated for 24 h under normal conditions. The luciferase activity was measured and normalized to β-galactosidase activity, and the data shown represent the mean ± SD (n = 3); *, P < 0.01 by Student's t test. (B) VSMCs were cotransfected with the plasmid encoding FLAG-tagged OGT (+) or vector control (−) and incubated for 24 h under normal glucose conditions. Immunoblotting (IB) for O-GlcNAc, NFκB p65, IκBα, VCAM-1, OGT, FLAG-OGT, and OGA was performed with the corresponding antibodies (1st, 2nd, 5th, and 8th–11th panels, respectively). NFκB p65 immunoprecipitates (IP) were analyzed for O-GlcNAc, NFκB p65, and IκBα (3rd, 4th, and 6th panels, respectively). Actin was used as a loading control (12th panel). (C) (Upper) VSMCs were immunostained by using antibodies against NFκB p65 to determine the subcellular localization. (Lower) OGT overexpression was detected with an anti-FLAG antibody conjugated to FITC. The percentages of cells showing NFκB p65 localization are derived from at least 150 transfected cells with FLAG-OGT in microscopic fields. (D) Immunoblotting of nuclear or cytosolic extracts of VSMCs by using antibodies against NFκB p65 was performed to determine NFκB p65 nuclear translocation (1st and 4th panels) or total levels of NFκB p65 (7th panel). The purity of the nuclear and cytosolic extracts was determined by immunoblotting of histone H2A (nuclear fractions, 2nd and 5th panels) and α-tubulin (cytosolic fractions, 3rd and 6th panels).