Fig. 2.
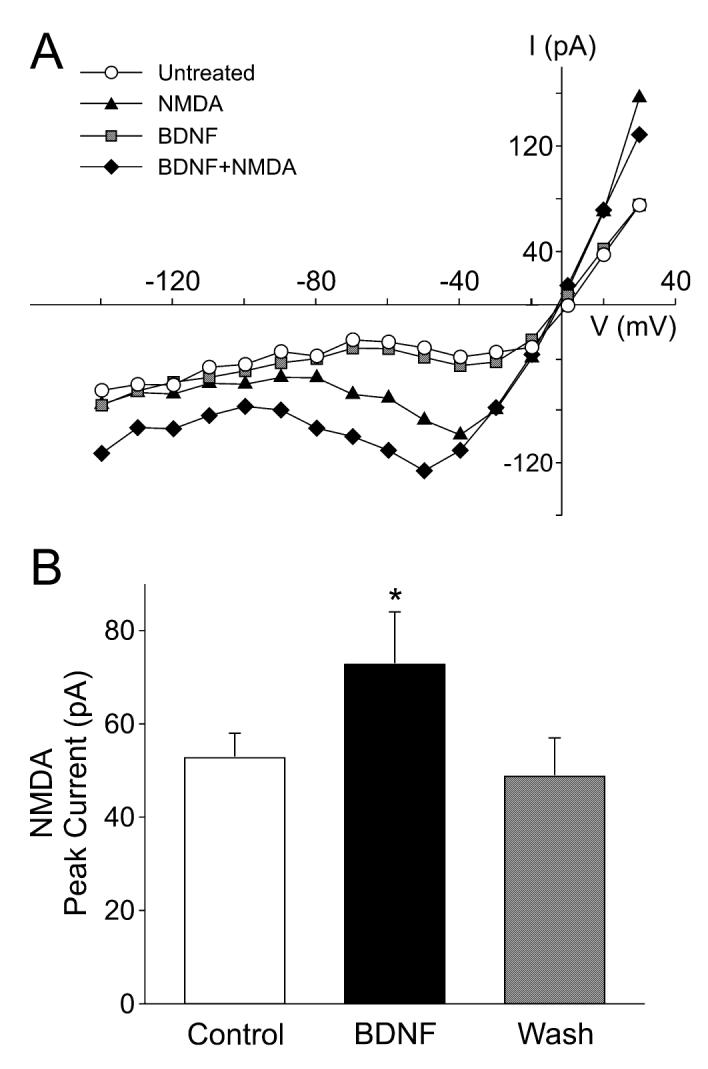
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) enhances the magnitude of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) currents in suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) neurons. Whole-cell patch-clamp recording techniques were used to measure currents evoked by NMDA in ventral SCN neurons during the night. The voltage dependence of the currents was measured by moving the membrane potential of the cell through a series of voltage steps before, during and after treatment with NMDA (25 μM, 120 s) or BDNF (100 ng/mL, 240 s) in the bath. (A) current—voltage relationship for peak NMDA currents recorded before (‘NMDA’) and after (‘BDNF + NMDA’) treatment. For comparison, the current—voltage curves obtained before any treatment (‘untreated’) and after BDNF alone (‘BDNF’) are shown. (B) Application of BDNF increased the magnitude of the peak NMDA currents. Control refers to NMDA-induced current before BDNF treatment. Neurons that did not respond to the BDNF treatment were not included in this analysis. Data are shown as means ± SEM. *Significance at P < 0.05.
