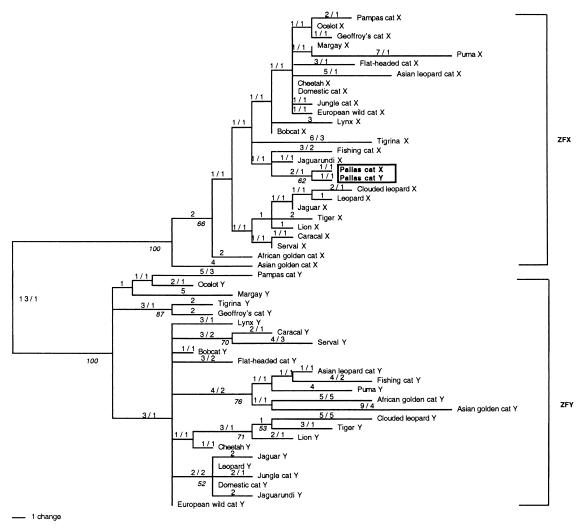
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic analysis using 1,181 bp of the Zn-finger exon of Zfx and Zfy for 26 species of Felidae. Shown is the 50% majority rule consensus (length = 171; consistency index = 0.672) of 10,850 trees generated by maximum parsimony analysis. Numbers on branches are length/homoplasies. Numbers in italics are bootstrap proportions in support of adjacent node that exceeded 50%. Bootstrap analysis consisted of 100 iterations (43). Note that the Zfx and Zfy sequences are respectively monophyletic with the exception of the pallas cat Y, which resembles X chromosomes Zfx genes and more precisely, the pallas cat Zfx homologue (see text). The resolution of species divergence hierarchies within the Zfx and Zfy groups are not robust because of slow-moving evolution of these genes in the period of Felidae evolution (10–15 million years). The derived tree is significantly different from a constrained tree representing established species lineages as listed in Fig. 2 (Kishino-Hasegawa test; t = 2.59; P < 0.0095). For this reason, the species topologies should not be considered to reflect Felidae phylogenetic divergence accurately.