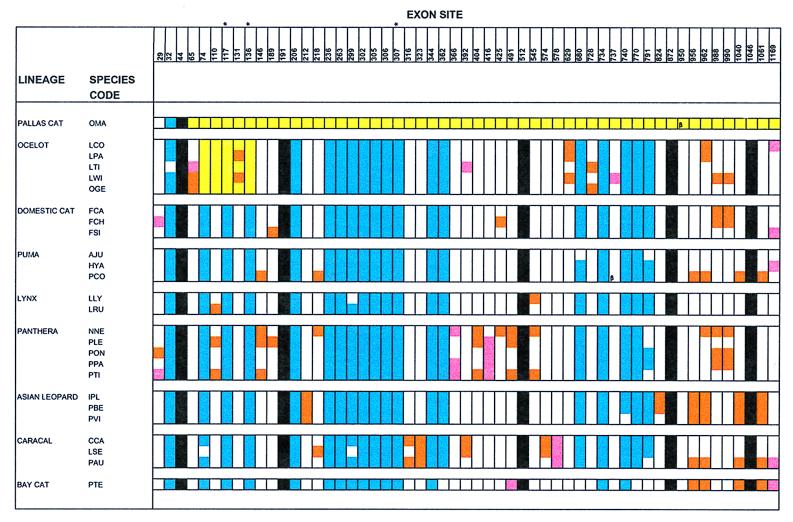
Figure 2.
Distribution of nucleotide sites that vary in two or more felid species in the Zn-finger exon of Zfy and Zfx. Except for the phylogenetically unaligned pallas cat, all other species are listed within the eight monophyletic evolutionary groups within Felidae (11–18). Five categories of substitutions are depicted. Blue: substitution diagnostic between Zfy and Zfx and fixed in the majority of species from all lineages. Black: Zfx-Zfy polymorphism, not sex specific. Orange: Newly derived Zfy substitution shared by some, or all, of the corresponding species group. Pink: Newly derived Zfx substitution shared by some, or all, of the corresponding species group. Yellow: Site where the Zfy-specific nucleotide is replaced by that from Zfx in some, or all of the corresponding species group. The yellow continuum for pallas cat includes those sites that are identical between Zfy and Zfx in most felid species (including pallas cat). In addition, the clearest evidence of gene conversion is that each of the fixed diagnostic sites (blue) shared by all other felid lineages are not present in the yellow region of Zfy exons from pallas cat or ocelot lineage species. Caracal group includes serval. β = Substitution that is unique and shared by Zfy and Zfx within a single species. *: Sites that encode amino acid substitutions distinguishing between Zfy and Zfx in all felids. For specific alignment details of polymorphic sites, please see Fig. 4 at PNAS web site http://www.pnas.org and http://lgd.nci.nih.gov.