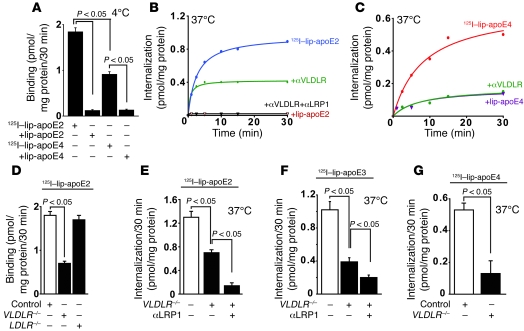
Figure 5. Isoform-specific lipo-apoE clearance at the abluminal surface of mouse brain capillaries in vitro is regulated by differential internalization rates of VLDLR and LRP1.
(A) Binding of 125I-labeled lipo-apoE2 and lipo-apoE4 (2 nM, TCA-precipitable 125I-radioactivity) to isolated brain microvessels. (B and C) Time-dependent internalization of 125I-labeled lipo-apoE2 (B) and lipo-apoE4 (C) in the presence of receptor-specific blocking antibodies against VLDLR and LRP1 and excess of unlabeled ligand at 0.5 μM. (D) Binding of 125I-labeled lipo-apoE2 to brain microvessels from control, VLDLR–/–, and LDLR–/– mice. (E–G) Internalization of 125I-labeled lipo-apoE2 (E), lipo-apoE3 (F), and lipo-apoE4 (G) at the abluminal surface of brain microvessels from control (white bars) and VLDLR–/– (black bars) mice studied for a period of 30 minutes. Means ± SEM, n = 3 experiments per group.