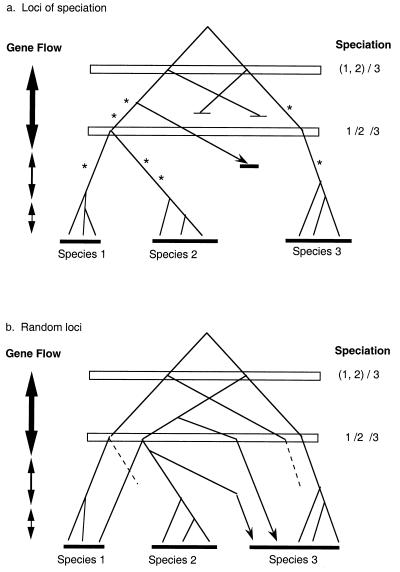
Figure 1.
Contrasting gene genealogies at two types of loci. Speciation occurred first between species 3 and the ancestor of species 1 and 2, and then between the latter species. Gene flow across species boundaries diminished with time. (a) “Speciation loci.” Each favorable mutation (marked with an *) drives the spread of a single lineage, excluding other lineages (ending with a tick). This would result in the purge of shared ancient polymorphisms. In addition, any lineage introgressed from the other species (arrow) is quickly eliminated because of the incompatibility with the new genetic background. Monophyly by species and a clear species phylogeny are observed. (b) “Other loci.” Ancient polymorphism and introgression during secondary contact (arrow) lead to mixed genealogies between species. Dashed branches denote lineages lost because of genetic drift. Note that species 2 and 3 appear most closely related.