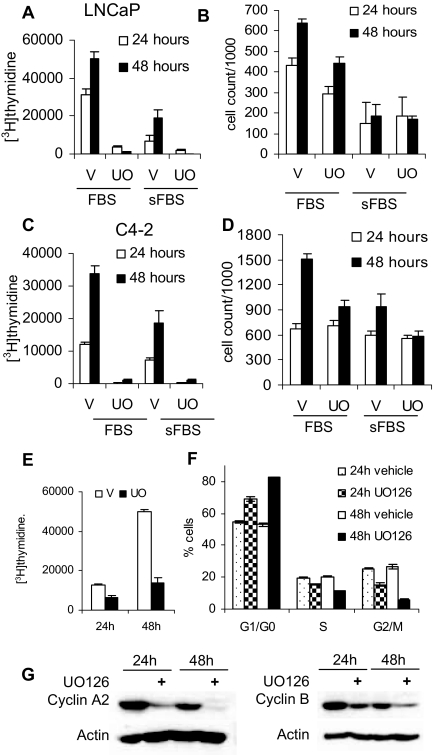
Figure 7.
UO126 Treatment Reduces Cell Proliferation and Induces G0/G1 Accumulation
A, LNCaP cells were plated at 1.5 × 105 cells per well in six-well plates in medium supplemented with 10% FBS. Cells were allowed to attach overnight and rinsed, and medium was substituted for one supplemented with either 10% sFBS or 10% FBS. Cells were then treated with either vehicle (V) (DMSO) or 20 μm UO126 (UO); 24 and 48 h later, cell proliferation was evaluated using [3H]thymidine incorporation. B, LNCaP cells were plated at 1.5 × 105 cells per well and treated in parallel with panel A and harvested at either 24 or 48 h and counted using the Coulter counter. C, C4-2 cells were plated at 1.5 × 105 cells per well in six-well plates. Cells were allowed to attach overnight, rinsed with serum free medium, and placed in a medium with either 5% sFBS or 5% FBS treated with DMSO or UO126 (UO) for 24 or 48 h, and proliferation was examined using [3H]thymidine incorporation. D, C4-2 cells were plated at 1.5 × 105 cells per well and treated in parallel with panel C. Cells were counted at the indicated time points using a Coulter counter. E, PC-3 cells were plated at 50,000 cells per well in six-well plates, treated with either DMSO or 20 μm UO126, and incubated for 24 or 48 h. Cell proliferation was measured using a [3H] thymidine incorporation assay. F, LNCaP cells were treated with either vehicle (DMSO) or 20 μm UO126 for 24 and 48 h. Cells were harvested, fixed with ethanol, stained with propidium iodide, and used for fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis to determine cell cycle distribution. G, LNCaP cells treated in parallel with F were used to analyze cyclin A2 and B expression by Western blotting.