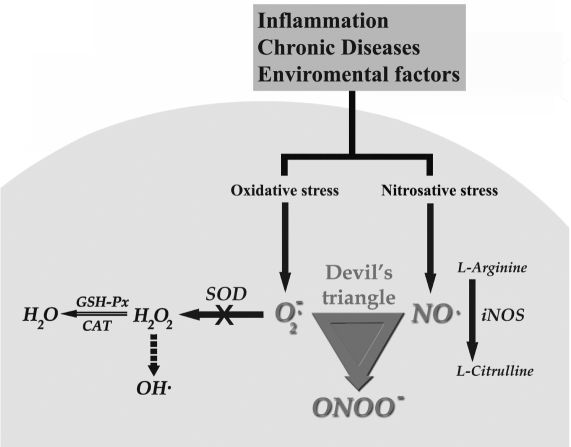
Figure 1.
Organization of the “devil’s triangle” within the targeted cell. UV, ionizing irradiation, smoking, hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia and chronic inflammation cause excess O2•− and NO production via several means. Normally, O2•− is readily degraded to H2O by intracellular enzymatic antioxidants. In the presence of abundant O2•− and iNOS-derived NO, the biochemically interaction of these substances inevitably produces vast amounts of ONOO− thereby reducing the degradation of O2•− by SOD. In early stages of oxidative stress, if iNOS is not fully activated, several conventional antioxidants including vitamin E and C diminish the damage via scavenging O2•− and thereby prevent the activation of the “devil’s triangle.” Unlike the classic antioxidant vitamins, melatonin is the only currently available molecule which is known to block all aspects of the “devil’s triangle” as well as to activate antioxidative enzymes at RNA expression level, thereby preventing the loss of essential cellular antioxidative ezymes.