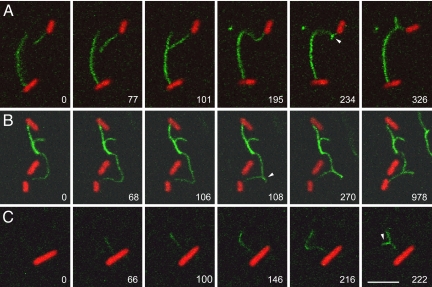
Fig. 4.
Supercoiling of F-pili during extension and retraction. This figure shows three examples in which extension of a pilus continues after its distal portion has become immobilized by binding to another pilus (A and B) or to the substratum (C). As each pilus continues to elongate, it curves in an arc, then abruptly generates a supercoil (arrowhead). After this transition, further extension of the pilus leads to elongation of the supercoiled segment (evident in all three time series), whereas retraction leads to shortening (B). All parameters are as described in Fig. 1 except that row C shows an F' lac strain. Each row of images consists of frames from a time series: (A) Movie S7; (B) Movie S8; (C) Movie S9. Time is shown as seconds after the first frame. (Scale bar, 5 μm; all images are at the same magnification.)