Abstract
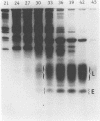
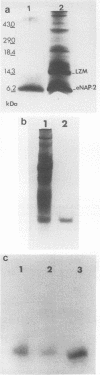
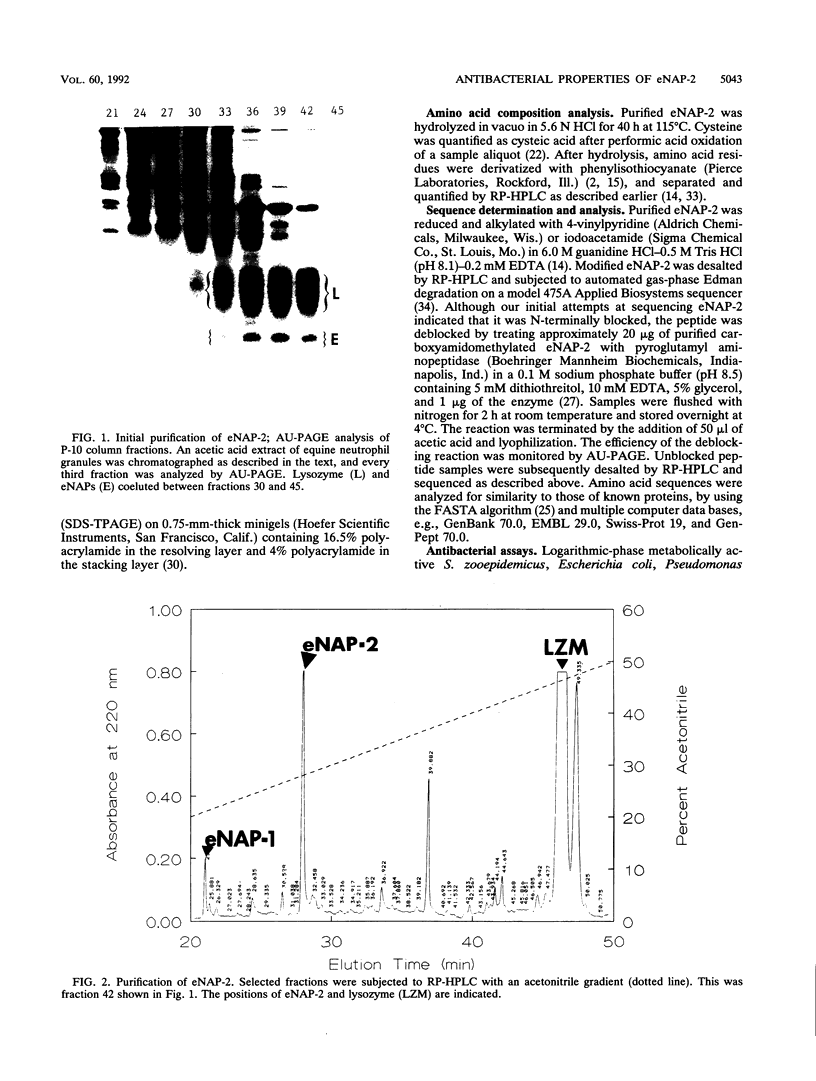
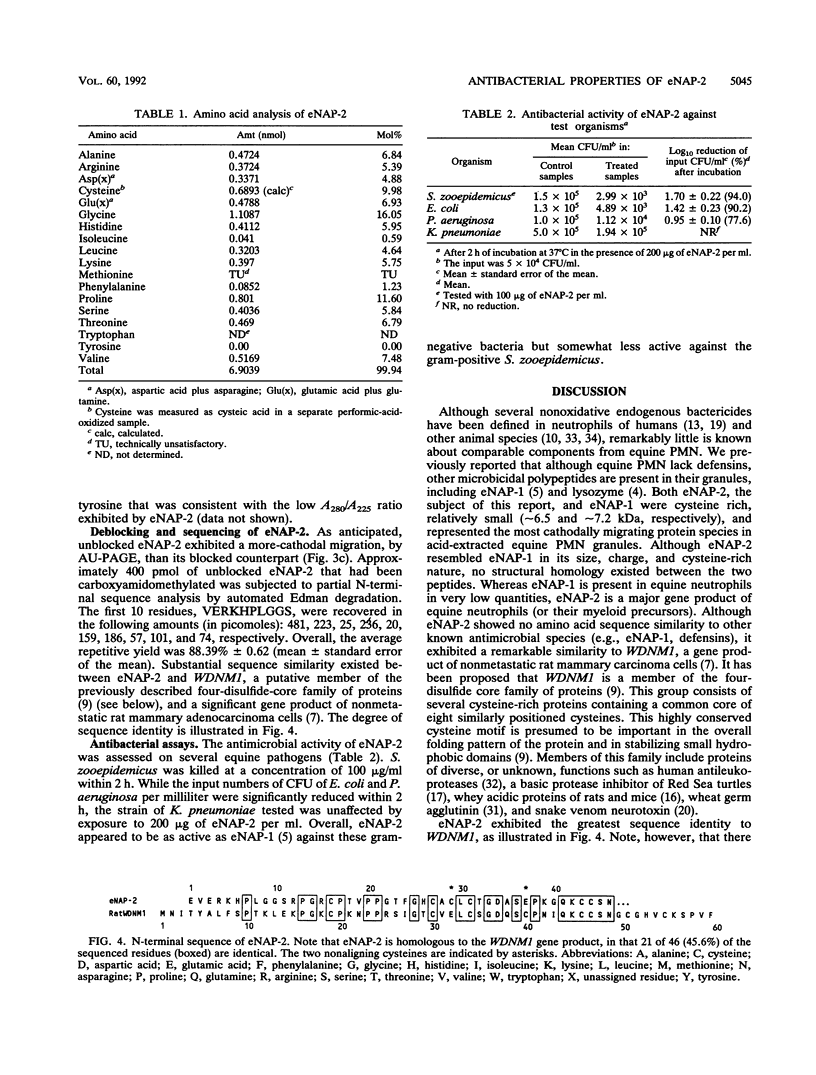
We purified a novel cysteine-rich antibiotic peptide, eNAP-2 (M(r), approximately 6,500), from acid extracts of equine neutrophils by sequential gel filtration and reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography and determined its partial N-terminal amino acid sequence. Although its cysteine motif distinguished eNAP-2 from all other currently known endogenous antibiotic peptides, including defensins and granulins, it showed substantial sequence similarity to WDNM1, a putative member of the four-disulfide-core protein family that also includes animal and human antiproteases, snake venom neurotoxins, and rat and mouse whey proteins. The antibacterial properties of eNAP-2 were tested against several equine uterine pathogens, namely, Streptococcus zooepidemicus, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Killing of S. zooepidemicus was very efficient, as evidenced by a 94% decrease in numbers of CFU per milliliter after exposure to 100 micrograms of eNAP-2 per ml (approximately 15 microM) for 2 h. Exposure of E. coli and P. aeruginosa to 200 micrograms of eNAP-2 per ml for 2 h resulted in 90.2 and 77.6% reduction, respectively, in the numbers of CFU per milliliter. Bacteriostasis, without bactericidal activity, occurred after K. pneumoniae was incubated with 200 micrograms of eNAP-2 per ml. Additional studies will be required in other species and cell types to determine whether eNAP-2 is restricted to equine neutrophils or is the index member of a larger family of endogenous antibiotics.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bateman A., Belcourt D., Bennett H., Lazure C., Solomon S. Granulins, a novel class of peptide from leukocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 31;173(3):1161–1168. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80908-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidlingmeyer B. A., Cohen S. A., Tarvin T. L. Rapid analysis of amino acids using pre-column derivatization. J Chromatogr. 1984 Dec 7;336(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)85133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A. The human neutrophil respiratory burst oxidase. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1140–1147. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couto M. A., Harwig S. S., Cullor J. S., Hughes J. P., Lehrer R. I. Identification of eNAP-1, an antimicrobial peptide from equine neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3065–3071. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3065-3071.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dear T. N., Ramshaw I. A., Kefford R. F. Differential expression of a novel gene, WDNM1, in nonmetastatic rat mammary adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Sep 15;48(18):5203–5209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond G., Zasloff M., Eck H., Brasseur M., Maloy W. L., Bevins C. L. Tracheal antimicrobial peptide, a cysteine-rich peptide from mammalian tracheal mucosa: peptide isolation and cloning of a cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3952–3956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drenth J., Low B. W., Richardson J. S., Wright C. S. The toxin-agglutinin fold. A new group of small protein structures organized around a four-disulfide core. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):2652–2655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenhauer P. B., Harwig S. S., Szklarek D., Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Lehrer R. I. Purification and antimicrobial properties of three defensins from rat neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2021–2027. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2021-2027.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank R. W., Gennaro R., Schneider K., Przybylski M., Romeo D. Amino acid sequences of two proline-rich bactenecins. Antimicrobial peptides of bovine neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):18871–18874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara S., Imai J., Fujiwara M., Yaeshima T., Kawashima T., Kobayashi K. A potent antibacterial protein in royal jelly. Purification and determination of the primary structure of royalisin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11333–11337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Szklarek D., Harwig S. S., Daher K., Bainton D. F., Lehrer R. I. Defensins. Natural peptide antibiotics of human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1427–1435. doi: 10.1172/JCI112120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrikson R. L., Meredith S. C. Amino acid analysis by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography: precolumn derivatization with phenylisothiocyanate. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennighausen L. G., Sippel A. E. Mouse whey acidic protein is a novel member of the family of 'four-disulfide core' proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 24;10(8):2677–2684. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.8.2677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert J., Keppi E., Dimarcq J. L., Wicker C., Reichhart J. M., Dunbar B., Lepage P., Van Dorsselaer A., Hoffmann J., Fothergill J. Insect immunity: isolation from immune blood of the dipteran Phormia terranovae of two insect antibacterial peptides with sequence homology to rabbit lung macrophage bactericidal peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):262–266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Ganz T. Antimicrobial polypeptides of human neutrophils. Blood. 1990 Dec 1;76(11):2169–2181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low B. W., Preston H. S., Sato A., Rosen L. S., Searl J. E., Rudko A. D., Richardson J. S. Three dimensional structure of erabutoxin b neurotoxic protein: inhibitor of acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):2991–2994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.2991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Furunaka H., Miyata T., Tokunaga F., Muta T., Iwanaga S., Niwa M., Takao T., Shimonishi Y. Tachyplesin, a class of antimicrobial peptide from the hemocytes of the horseshoe crab (Tachypleus tridentatus). Isolation and chemical structure. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16709–16713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Chalkley R. High resolution acrylamide gel electrophoresis of histones. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini A., Hägeli G., von Fellenberg R. Isolation and characterization of three protein proteinase isoinhibitors from the granular fraction of horse neutrophilic granulocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 15;154(3):1107–1113. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90255-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podell D. N., Abraham G. N. A technique for the removal of pyroglutamic acid from the amino terminus of proteins using calf liver pyroglutamate amino peptidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Mar 15;81(1):176–185. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91646-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rausch P. G., Moore T. G. Granule enzymes of polymorphonuclear neutrophils: A phylogenetic comparison. Blood. 1975 Dec;46(6):913–919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo D., Skerlavaj B., Bolognesi M., Gennaro R. Structure and bactericidal activity of an antibiotic dodecapeptide purified from bovine neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9573–9575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemüller U., Arnhold M., Fritz H., Wiedenmann K., Machleidt W., Heinzel R., Appelhans H., Gassen H. G., Lottspeich F. The acid-stable proteinase inhibitor of human mucous secretions (HUSI-I, antileukoprotease). Complete amino acid sequence as revealed by protein and cDNA sequencing and structural homology to whey proteins and Red Sea turtle proteinase inhibitor. FEBS Lett. 1986 Apr 7;199(1):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81220-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Brown D. M., DeLange R. J., Harwig S. S., Lehrer R. I. Primary structures of six antimicrobial peptides of rabbit peritoneal neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4579–4584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Harwig S. S. Purification, primary structure, and antimicrobial activities of a guinea pig neutrophil defensin. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2281–2286. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2281-2286.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitznagel J. K., Shafer W. M. Neutrophil killing of bacteria by oxygen-independent mechanisms: a historical summary. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 May-Jun;7(3):398–403. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.3.398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. S. The crystal structure of wheat germ agglutinin at 2-2 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1977 Apr 25;111(4):439–457. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]