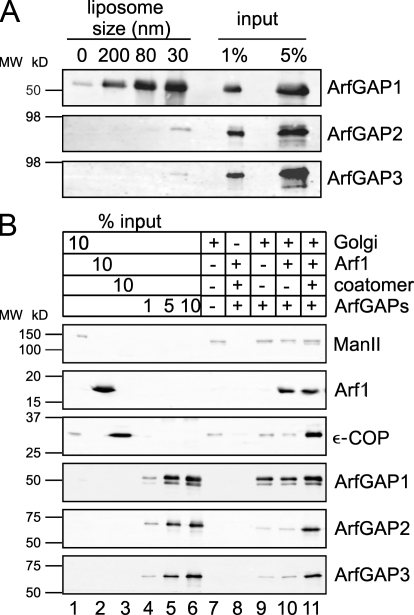
Figure 4.
Binding of ArfGAPs to membranes. (A) Binding of ArfGAPs to liposomes of different sizes. ArfGAPs were mixed with liposomes (extruded through 200-, 80-, or 30-nm filters, or no liposomes as a control) to a final concentration of 0.5 μM of protein and 0.5 mM of lipids in a total volume of 200 μl. After 5 min of incubation at RT, the samples were floated to an interphase between 25 and 0% (wt/vol) sucrose. 10% of the collected fractions were analyzed for the presence of ArfGAPs by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with specific antibodies against ArfGAP1, ArfGAP2, and ArfGAP3 and were compared with 1 and 5% of the input. (B) Binding of ArfGAPs to Golgi membranes. Rat liver Golgi membranes were incubated with ArfGAP proteins, myristoylated Arf1, coatomer, and the slowly hydrolyzable GTP analogue GTPγS in the combinations indicated. Golgi membranes were pelleted through a 20% (vol/vol) sucrose cushion, and 30% of the sample was analyzed for bound proteins by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with antibodies directed against the indicated proteins. MW, molecular weight.