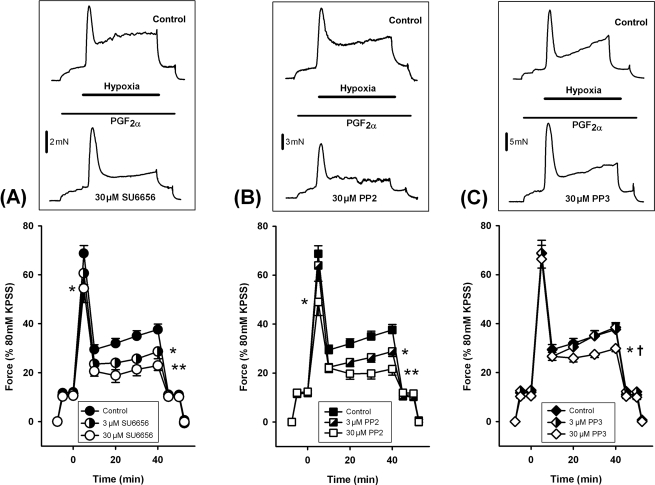
Figure 1.
Effects of src-family kinase (srcFK) inhibitors on hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction in intra-pulmonary arteries. Intra-pulmonary arteries were pre-constricted with PGF2α before being made hypoxic. Example traces (top panels) show the effects of hypoxia first in the absence (upper trace), and then in the presence (lower trace) of inhibitors. The sustained phase contraction was inhibited by the srcFK inhibitors SU6656 [(A) 3 µM, 33 ± 10% block, *P < 0.05, n = 8 arteries; 30 µM, 56 ± 6% block, **P < 0.001, n = 8 arteries] and PP2 [(B) 3 µM, 37 ± 6% block, *P < 0.01, n = 10 arteries; 30 µM, 64 ± 9% block, **P < 0.001, n = 10 arteries]. The inactive analogue PP3 also partially inhibited the sustained phase at 30 µM [(C) 28 ± 6% block, *P < 0.05, n = 8 arteries], but this effect was significantly less than for PP2 (†P < 0.01 vs. 30 µM PP2); PP3 had no effect at 3 µM. The transient phase was partially inhibited by SU6656 (30 µM, 23 ± 10% block, *P < 0.01) and PP2 (30 µM, 35 ± 9% block, *P < 0.01).