Fig. 2.
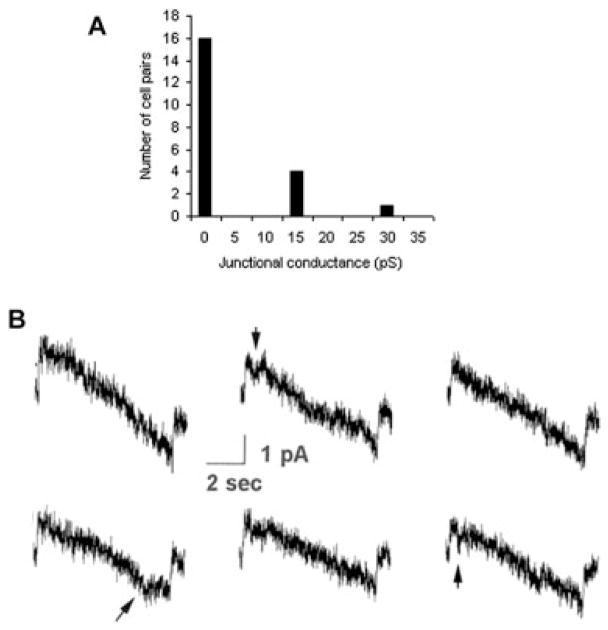
Electrophysiology shows functional coupling between pairs of microglia consistent with the properties of Cx36 channels. A: Summary of junctional conductance (gj) measurements obtained in 23 pairs of mouse neocortical microglial cells. Seven of twenty-three pairs were measurably coupled; although gj was generally quite low, it exceeded 5 nS in two cell pairs (not illustrated). B: Transjunctional currents recorded between pairs of human microglial cells in response to voltage ramps ±100 mV. Junctional currents were small, corresponding to junctional conductances of 10–15 pS. In addition, transitions were occasionally seen, corresponding to similar change in conductance. Junctional conductance was only very poorly voltage dependent, as indicated by the lack of transition at high positive or negative Vj values. Arrows indicate Cx36-like channel activity.