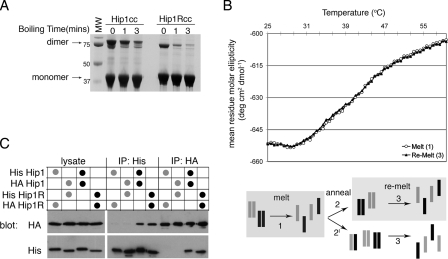
FIGURE 2.
Hip1 and Hip1R are stable homodimers. A, Hip1cc or Hip1Rcc, amino acids 361-637 and 346-655, respectively, were expressed and purified. Purified Hip proteins were diluted into reducing SDS-PAGE loading buffer and run on an SDS-polyacrylamide gel after boiling for the indicated times. The migration positions of monomers and dimers and molecular weight (MW) markers (in kDa) are indicated. B, circular dichroism melting analysis of a 1:1 mixture of Hip1cc and Hip1Rcc. Shown is the molar ellipticity versus temperature as determined by monitoring the change in helical content of proteins at 222 nm. Homodimers of Hip1 and Hip1R were mixed at a 1:1 ratio, and then a thermal denaturation profile was obtained (corresponding to melting step 1 in the diagram; open circles). The mixture of denatured proteins was allowed to anneal slowly back to 20 °C (step 2 or 2′ in the diagram). The thermal denaturation profile was collected for the newly annealed population (step 3 in the diagram; filled triangles). Both melting curves precisely overlap, showing that path 2 (not 2′) was the primary route followed. C, co-immunoprecipitation of His- or HA-tagged full-length Hip1 or Hip1R. HeLa cells were co-transfected with the two constructs indicated in the table above the blot to achieve equivalent levels of expression of each construct. HeLa cells were lysed, and tagged Hip proteins were isolated by immunoprecipitation (IP) with either anti-His antibody or anti-HA antibody as shown. Immunoprecipitates and transfected cell lysate were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose for immunoblotting. Nitrocellulose membranes were probed with anti-His, stripped, and then probed with anti-HA. Black dots indicate homotypic transfection combinations. Gray dots indicate heterotypic transfection combinations.