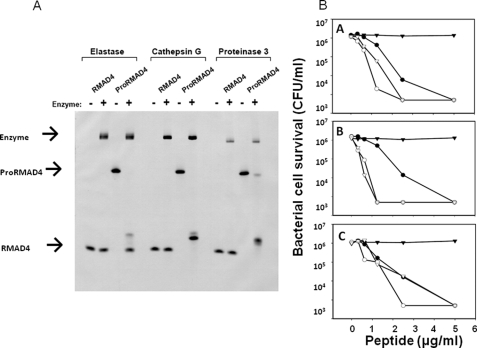
FIGURE 1.
In vitro cleavage and activation of proRMAD-4(20–94) by NE, CG, and P3. In A, samples of proRMAD-4(20–94) (10 μg) were incubated overnight in vitro with (+) or without (–) NE, CG, and P3, and digests were resolved by AU-PAGE and stained with Coomassie Blue (see “Experimental Procedures”). proRMAD-4(20–94) is digested by NE, and the digested product runs alongside native RMAD-4(62–94). CG and P3 digest proRMAD-4(20–94), and the products have lower mobilities in AU-PAGE analysis. In B, bactericidal activities against S. typhimurium ΔphoP of recombinant proRMAD-4(20–94), RMAD-4(62–94), and the complete digests of proRMAD-4(20–94) incubated with each of the azurophil granule serine proteases. Panels A, peptides exposed to NE; B, peptides exposed to CG; C, peptides exposed to P3. Symbols:(-▾-), proRMAD-4(20–94) with no serine protease; (-○-), proRMAD-4(20–94) with serine protease; (-▿-), RMAD-4(62–94) with no serine protease; (-•-), RMAD-4(62–94) exposed to serine protease. proRMAD-4(20–94) lacks bactericidal activity, native RMAD-4(62–94) is bactericidal. The three serine proteases convert inactive proRMAD-4(20–94) to a bactericidal molecule.