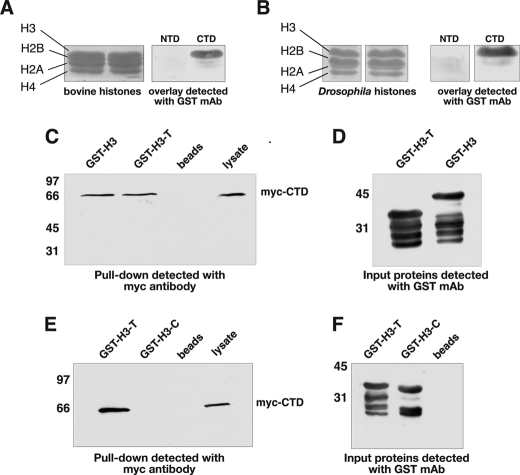
FIGURE 6.
The CTD domain of JIL-1 interacts with the tail region of histone H3. In overlay experiments purified bovine histones (A) and Drosophila histone extractions from S2 cells (B) were fractionated by SDS-PAGE, immunoblotted, and incubated with JIL-1 NTD or CTD GST fusion protein, and interactions were detected with a GST mAb (right panels). Ponceau S labeling of the fractionated histone proteins is shown in the left panels. In pulldown experiments (C and E) lysate from S2 cells stably expressing an Myc-tagged CTD domain of JIL-1 (Myc-CTD) and incubated with GST-histone H3 fusion constructs (GST-H3, GST-H3-T, and GST-H3-C) or with beads-only was pelleted with glutathione-agarose beads, and the interacting proteins were fractionated by SDS-PAGE, immunoblotted, and probed with Myc antibody. Unincubated S2 cell lysate was included as a control (right lanes). In these experiments interactions between JIL-1 Myc-CTD and GST-H3 as well as GST-H3-T were detected but not with GST-H3-C. D and F, immunoblots of the GST fusion proteins used for the pulldown experiments in C and E were detected with GST antibody. The relative migration of molecular size markers is indicated to the left of the immunoblots in kDa.