Figure 1.
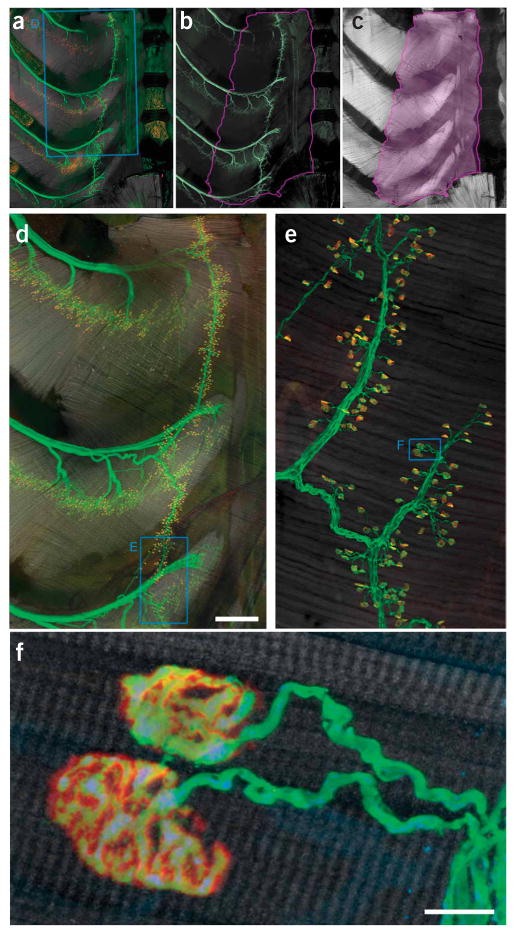
Innervation pattern of the triangularis sterni muscle. (a–c) Triangularis sterni muscle and its innervation in a thy1–YFP16 mouse with YFP-labeled axons18. (a) Combined labeling of axons (green), synapses (red) and muscle (gray scale). (b) Axonal labeling. (c) Muscle stain. The violet line in b and c outlines the triangularis sterni muscle between the inner surface of the sternum to the proximal rib cage. (d) Confocal reconstruction of the area boxed in a, showing the multisegmental innervation of the triangularis sterni muscle. (e) High-power confocal reconstruction of a part of the endplate band (boxed area in d). (f) Confocal image showing two individual neuromuscular junctions boxed in e. Accumulations of mitochondria can be found in presynaptic terminals. YFP (axonal cytoplasm), green; BTX (acetylcholine receptors), red; phalloidin (muscle), gray scale. Scale bars, 500 μm in d and 10 μm in f.
