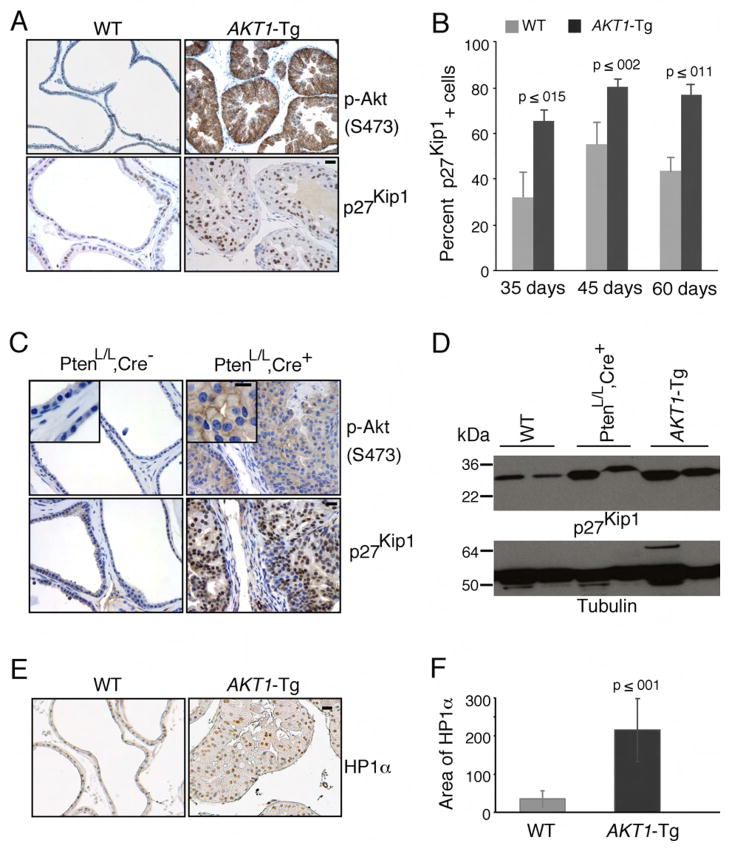
Figure 1. Induction of p27Kip1 and senescence in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia of AKT1-Tg and PtenL/L;Cre+ mice.
(A) VPs from wild-type (WT) and AKT1-Tg mice were stained by immunohistochemisty using antibodies directed against phospho-Akt (S473) (upper panel) or against p27Kip1 (lower panel). Scale bar, 50 μM
(B) The number of p27kip1 positively staining cells was determined in the VPs of wild type (WT) and AKT1-Tg mice of the indicated ages. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.
(C) Wild type (PtenL/L;Cre−) and Pten conditional knock out (prostate specific) (PtenL/L;Cre+) VPs were stained with phospho-Akt (S473) (upper panel) or anti-p27Kip1 (lower panel). Scale bar, 50 μM; insert 100μM
(D) Western blot analysis of p27Kip1 and Tubulin in whole cell lysates from ventral prostates of Wild type (WT), AKT1-Tg and Pten conditional knock out (PtenL/L;Cre+) mice of 6 weeks old
(E) VPs from wild type and AKT1-Tg mice were stained with antibody against HP1α. Scale bar,50μM.
(F) Area of HP1α staining were measured both in wild type and AKT1-Tg prostates. Data are presented as mean ± SD.