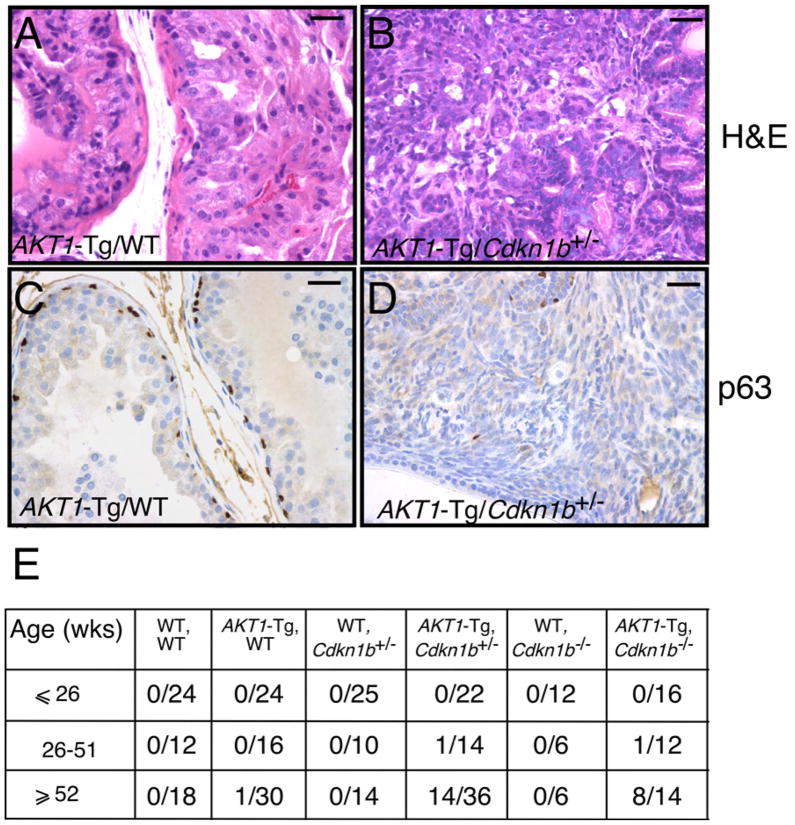
Figure 3. Genetic inactivation of Cdkn1b in AKT1-Tg mice results in the development of invasive prostate cancer.
(A) Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia in a representative section from the VP of AKT1-Tg mouse (~52 weeks old). Scale bar, 100 μM
(B) Invasive prostate cancer in representative sections from AKT1-Tg/Cdkn1b+/−. Sections were stained with H&E. Scale bar, 100 μM
(C) VP from AKT1-Tg mice were stained with antibodies directed against p63. Scale bar, 100 μM
(D) VP from AKT1-Tg/Cdkn1b+/− mice were stained with antibodies directed against p63. Scale bar, 100 μM
(E) Summary of tumor incidence by age and genotype.