Fig. 4.
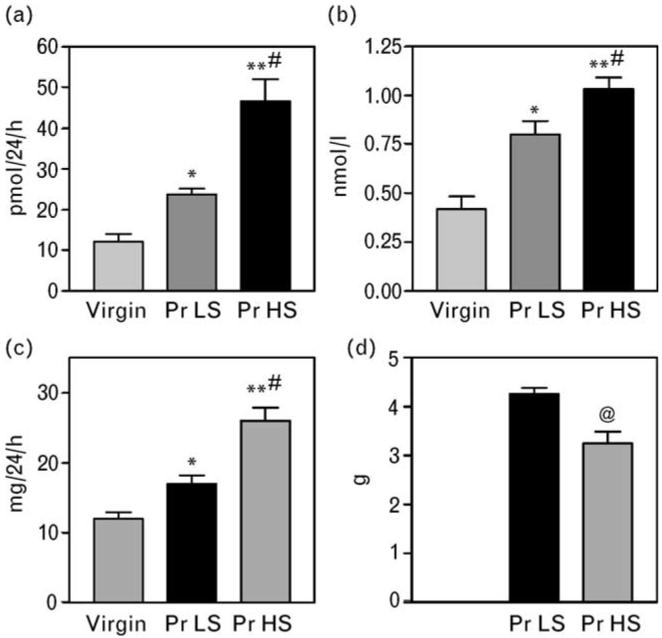
Renal excretion (a) and plasma concentration (b) of MBG and renal protein excretion (c) in virgin rats, and in pregnant rats with (Pr HS) or without (Pr LS) NaCl supplementation (day 19 of gestation). Means± SEM from 8–10 observations. By one-way ANOVA followed by Newman–Keuls test: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 vs. virgin rats. #P < 0.01 vs. Pr LS. (d) Mean weight of pups from Pr LS and Pr HS; @P < 0.01 vs. Pr LS, two-tailed t-test. MBG, marinobufagenin; Pr HS, pregnant rats with high-salt intake; Pr LS, pregnant rats with low-salt intake.
