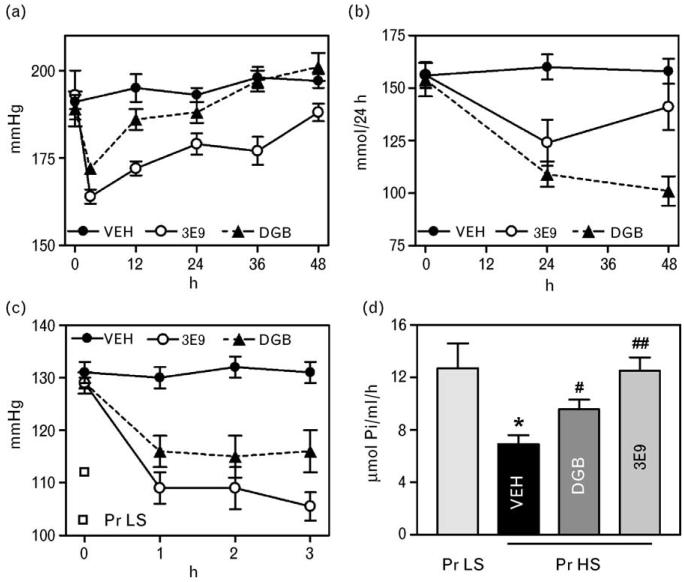
Fig. 6.
Systolic blood pressure (a) and renal sodium excretion (b) in hypertensive Dahl-S rats following single intraperitoneal administration of vehicle (VEH), 3E9 mAb, and Digibind (DGB). Repeated measures ANOVA followed by Newman–Keuls test. Systolic blood pressure: VEH vs. 3E9; P < 0.001; VEH vs. DGB; P < 0.05; 3E9 vs. DGB; P < 0.001. Renal sodium excretion: VEH vs. 3E9; P < 0.05; VEH vs. DGB; P < 0.01; 3E9 vs. DGB; P < 0.05. Systolic blood pressure (c) and activity of NKA in erythrocytes in NaCl-supplemented rats following single intraperitoneal administration of vehicle (VEH), 3E9 mAb, and DGB. Repeated measures ANOVA followed by Newman–Keuls test. Systolic blood pressure: VEH vs. 3E9; P < 0.001; VEH vs. DGB; P < 0.05; 3E9 vs. DGB; P < 0.001. One-way ANOVA followed by Newman–Keuls test: *P < 0.01 vs. pregnant rats on a low NaCl intake (PrLS); #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. vehicle (VEH). DS, Dahl-S rats Pr HS, pregnant rats with high-salt intake; Pr LS, pregnant rats with low-salt intake.