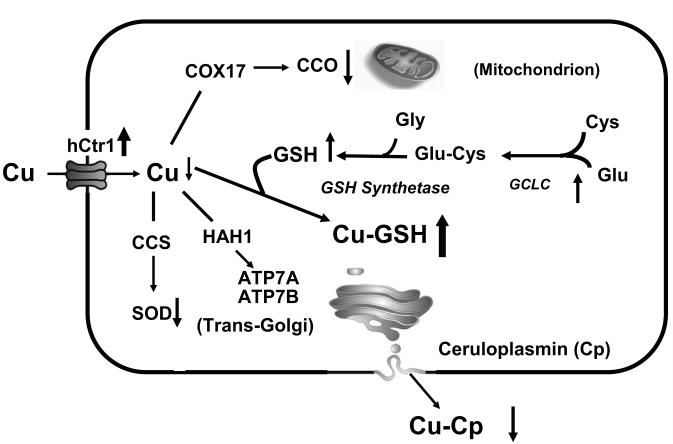
Fig. 7.
Schematic illustration showing the effects of GCLC overexpression on cellular Cu metabolism. Overexpression of GCLC, which catalyzes the ligation of cysteine (Cys) and glutamate (Glu), results in increased GSH levels. Excess GSH functions as a Cu depletor, as evidenced by the reduction of CCO and SOD activity, and holo-ceruloplasmin (Cu-Cp) contents. Intracellular Cu deficiency upregulates hCtr1 expression resulting in elevated sensitivity to CDDP treatment. CCS, HAH1, and COX17 are Cu chaperones that shuffle Cu to their respective targets as indicated by arrows.