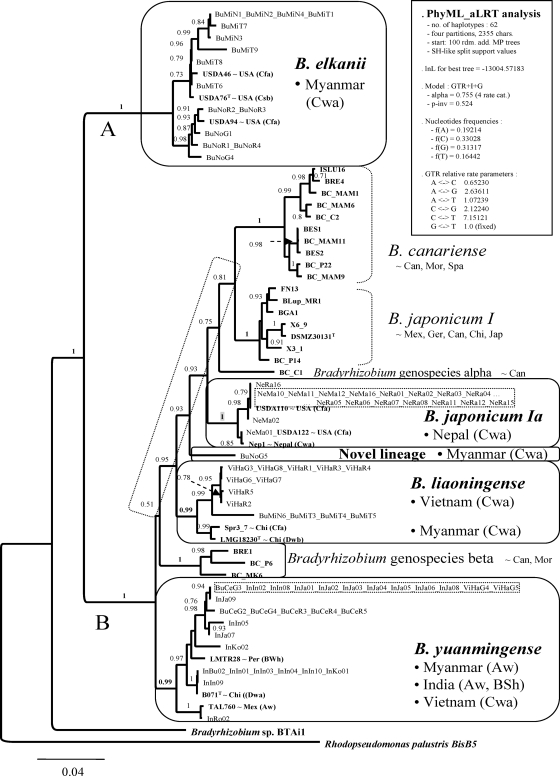
FIG. 1.
ML species tree estimated under the GTR-I-G model, showing the relationships among 62 atpD-glnII-recA-rpoB haplotypes found among 76 Asiatic Bradyrhizobium isolates and 34 reference strains (bold). This was the best tree found among 101 independent PhyML searches started from 100 random sequential addition trees and 1 NJ seed tree. The support values on the bipartitions correspond to SH-like P values, which denote the probability of the particular branch being correct. Ten Bradyrhizobium sp. lineages were resolved. The Asiatic isolates grouped in five of them, which are enclosed in rounded boxes. Dotted boxes highlight epidemic clones. The vertical rectangular box shows the parameterization of the PhyML tree search resulting in the best ln L score. The scale indicates the expected number of substitutions per site under the specified substitution model. The following country or regional abbreviations were used to indicate the geographic origins of the reference strains: Can, Canary Islands; Chi, China; Ger, Germany; Jap, Japan; Mex, Mexico; Mor, Morocco; Per, Peru; Spa, Spain; USA, United States. The following abbreviations were used to indicate the Köppen-Geiger world climate classes: BWh, dry, arid, hot; Cfa, humid, temperate, without dry season and hot summer; Csb, humid, temperate, with dry cool summer; Dwa, humid, cold, with dry winter and hot summer; Dwb, humid, cold, with dry winter and cool summer. The remaining abbreviations are explained in Table 1.