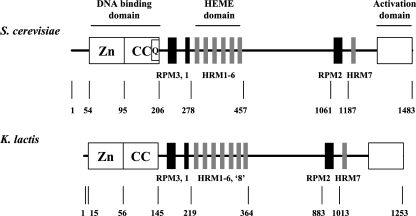
FIG. 1.
Comparison of functional modules between S. cerevisiae Hap1p and K. lactis KlHap1p. Both proteins are schematically represented and composed of a typical Zn(II)2Cys6 binuclear cluster (box Zn) followed by a coiled-coil dimerization domain (box CC), three repression modules (RPM; indicated with solid bars), several heme-responsive modules (HRM; indicated with stippled bars; seven in S. cerevisiae and eight in K. lactis), and an activation domain (box at C terminus). The stretch of 12 glutamine residues (box Q) present in the C-terminal part of the dimerization domain in Hap1p is absent in KlHap1p. Numbers indicate amino acid residue positions in the proteins. The distances are not in proportion.