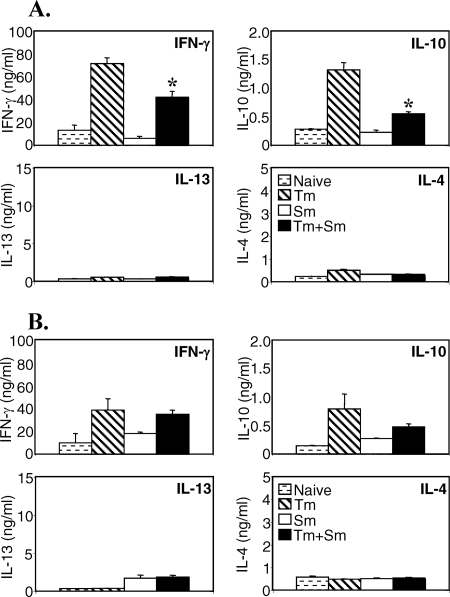
FIG. 2.
Concurrent S. mansoni (Sm) infection modulates the cytokine response to T. muris (Tm) in the spleen. AKR mice were infected orally with 150 T. muris eggs, percutaneously with 50 S. mansoni cercariae, or both. S. mansoni infection was started 40 days after T. muris infection. Mice were sacrificed 7 weeks after S. mansoni infection. Spleen (A) and MLN (B) cells from uninfected (stippled bars), T. muris-infected (hatched bars), S. mansoni-infected (white bars), or S. mansoni- and T. muris-coinfected (black bars) mice were removed and stimulated in vitro with T. muris antigen. Supernatants were analyzed by sandwich ELISA for the presence of IFN-γ, IL-10, IL-13, and IL-4. Means of five mice per group and standard errors of the mean are shown. Data from one representative experiment out of three are shown. *, statistically significant difference between T. muris singly infected and coinfected groups (P < 0.05).