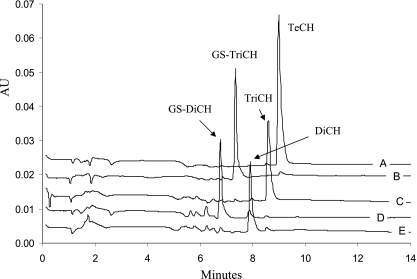
FIG. 2.
HPLC chromatograms of sequential reactions of TeCH transformation by PcpC C14S and PcpF. Reactions were carried out in 100 μl of 70 mM KPi buffer (pH 6.5) containing 2 mM ascorbic acid, 10 mM GSH, and 200 μM TeCH. (A) Reaction mixture only. A total of 20 μl of sample was removed, mixed with 20 μl of acetonitrile-acetic acid (9:1), centrifuged, and analyzed by HPLC. (B) Reaction mixture after the first PcpC C14S catalysis. Two microliters of PcpC C14S (ultracentrifuged cell extracts, 27.6 mg/ml) was added to the remaining 80 μl of reaction mixture, which was incubated at 30°C for 2 min and then heated at 65°C for 5 min before HPLC analysis of 20 μl of sample as described above. (C) Reaction mixture after the first PcpF catalysis and heat inactivation. One microliter of PcpF (2 mg/ml) was added to the remaining sample of reaction mixture B, which was incubated at 30°C for 2 min and then heated at 65°C for 10 min before HPLC analysis of 20 μl of sample as described above. (D) Reaction mixture after the second PcpC C14S (1 μl) catalysis and heat inactivation. (E) Reaction mixture after the second PcpF (0.5 μl) catalysis. HPLC data were extracted at 300 nm and exported in ASCII format and analyzed by Microsoft Excel. The chromatograms were separated by adding a constant of 0.005, 0.010, 0.015, 0.020, or 0.025 to the corresponding set of absorption unit (AU) data.