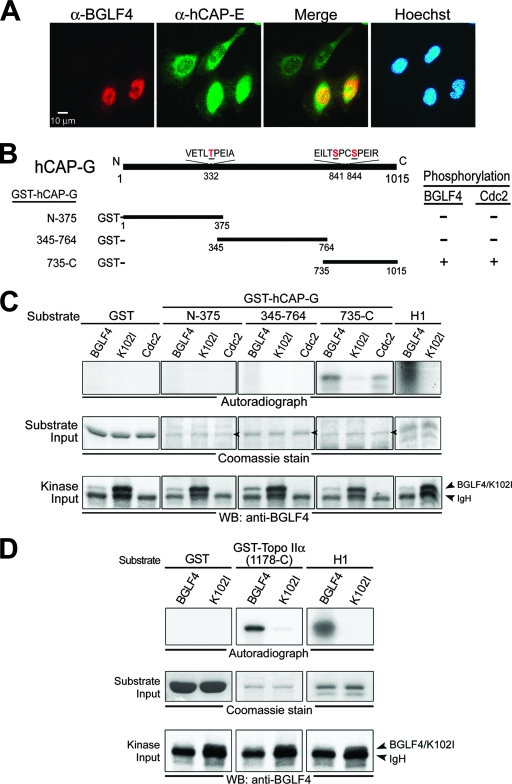
FIG. 1.
BGLF4 phosphorylates the condensin hCAP-G subunit and Topo IIα in vitro. (A) HeLa cells were transfected with a BGLF4-expressing plasmid. At 24 h posttransfection, cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and stained for BGLF4 (red), condensin hCAP-E (green), and DNA (blue) as described in Materials and Methods. BGLF4 induces hCAP-E nuclear accumulation and colocalizes with hCAP-E (yellow in the merge image) in the nucleus of transfected cells. (B) Schematic representation of human condensin hCAP-G protein. Three plasmids expressing GST fusion condensin protein, GST-hCAP-G(N-375), GST-hCAP-G(345-764) and GST-hCAP-G(735-C), were constructed and expressed in E. coli BL21(DE3) (data not shown). Putative BGLF4 and Cdc2 target sites Thr-332, Ser-841, and Ser-844 on condensin and the abilities of BGLF4 and Cdc2 to phosphorylate the condensin hCAP-G subunit are indicated. (C) Lysates from nocodazole-treated HeLa cells or insect Sf9 cells infected with BGLF4 or K102I recombinant baculovirus were immunoprecipitated with anti-Cdc2 or anti-BGLF4 2224 antibody. The immunoprecipitates then were incubated with kinase buffer containing [γ-32P]ATP in the presence of purified GST, GST-hCAP-G(N-375), GST-hCAP-G(345-764), GST-hCAP-G(735-C), or histone H1 at 30°C for 30 min. After proteins were resolved by 10% SDS-PAGE, gels were stained with Coomassie blue, dried, and subjected to autoradiography or transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane and probed with anti-BGLF4 2616 antibody to detect the kinase input. The phosphorylation of histone H1 by BGLF4 served as a positive control for the kinase reaction. (D) The IP kinase assay was performed using recombinant baculovirus-infected Sf9 lysates and purified GST, GST-Topo IIα(1178-C), or histone H1 protein as the substrate. WB, Western blot.