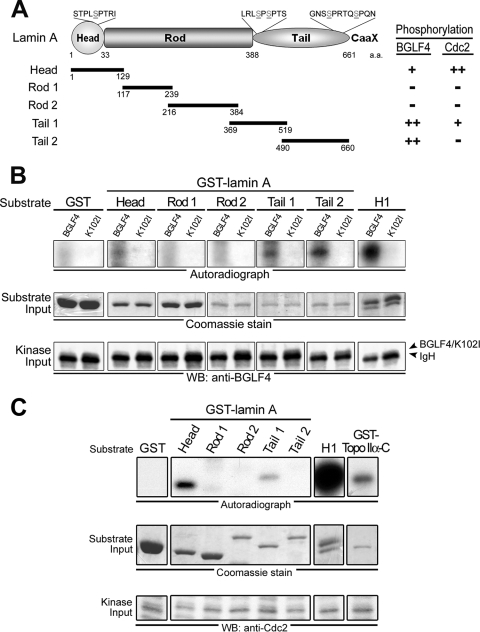
FIG. 3.
BGLF4 phosphorylates lamin A in vitro. (A) Structurally, human lamin A protein is composed of amino-terminal head, central rod, and carboxyl-terminal tail domains. GST-fused distinct fragments of lamin A (Head, aa 1 to 129; Rod 1, aa 117 to 239; Rod 2, aa 216 to 384; Tail 1, 369 to 519; Tail 2, aa 490 to 660) were expressed in E. coli and purified (data not shown). Putative BGLF4 and Cdc2 target sites on GFP-lamin A, including Ser-22, Ser-390, Ser-392, Ser-652, and Ser-657, are indicated. (B) BGLF4 or K102I proteins from insect Sf9 cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-BGLF4 2224 antibody. The IP kinase assay was performed by using purified GST, five GST-lamin A protein fragments, or histone H1 as the substrate. The results of the kinase reaction were analyzed as described in the legend to Fig. 1C. (C) Cellular Cdc2 phosphorylates lamin A and Topo IIα in vitro. HeLa cells were treated with nocodazole (100 ng/ml) for 20 h, harvested using the mechanical shake-off method, and lysed in IP buffer as described in Materials and Methods. Subsequently, IP kinase assays were performed using antibody against Cdc2 to precipitate endogenous Cdc2 kinase and purified GST-lamin A protein fragments or GST-Topo IIα(1178-C) as the kinase assay substrate. Histone H1 phosphorylation by BGLF4 served as a positive control in the kinase reaction. Inputs of kinase and the substrate were detected by anti-Cdc2 antibody or Coomassie blue staining. Cdc2 phosphorylates lamin A at Head and Tail 1 domains and phosphorylates Topo IIα at the carboxyl-terminal region. WB, Western blot.