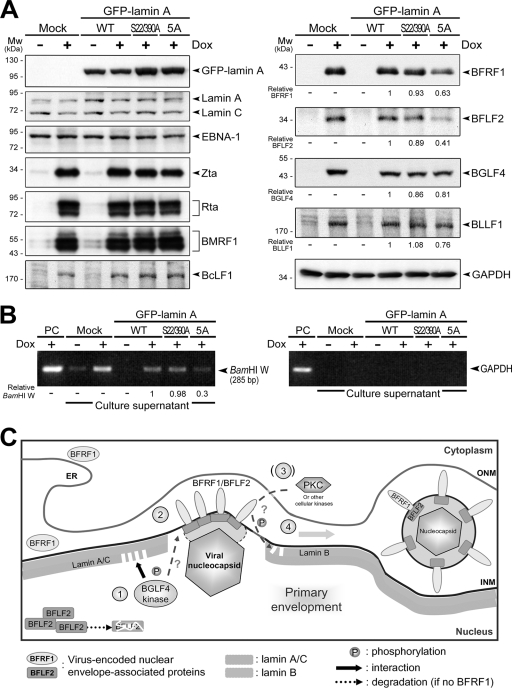
FIG. 6.
Expression of lamin A with mutations at BGLF4 target sites reduces EBV BFRF1/BFLF2 protein expression and virion production. (A) EBV-positive tetracycline-inducible EREV8 cells were mock transfected or were transfected with plasmids expressing GFP-lamin A(WT), GFP-lamin A(S22/390A), or GFP-lamin A(5A). At 12 h posttransfection, cells were incubated with 100 ng/ml doxycycline (Dox) to induce the expression of Rta and subsequent EBV reactivation. The cells were harvested and subjected to immunoblotting analysis at 72 h postinduction. The protein expression was detected by anti-GFP JL-8, anti-lamin A/C 636, NPC-47 serum (for EBNA-1), anti-Zta 4F10, anti-Rta 467, anti-BMRF1 88A9, anti-BcLF1 L2, anti-BFRF1 E10, anti-BFLF2 C1, anti-BGLF4 2616, or anti-BLLF1 201 in immunoblotting. GAPDH served as a loading control. Mw, molecular mass. (B) The culture supernatants were centrifuged to harvest secreted EBV virions. The isolated viral particles were lysed and subjected to PCR analysis targeting the EBV DNA BamHI W fragment. The lack of GAPDH DNA rules out the possibility of cellular DNA contamination. PC, lysate from EREV8 cells that served as a PCR positive control. (C) A hypothetical model of the nuclear egression of EBV nucleocapsids. After EBV replication and genome encapsidation, the viral nucleocapsid moves close to the inner nuclear lamina. Simultaneously, lamina-targeted BGLF4 first induces the redistribution of lamin A/C adjacent to the nucleoplasm through direct phosphorylation (step 1) and consequently stabilizes BFLF2 protein by enhancing the interaction between nuclear envelope-associated BFRF1 and intranuclear BFLF2 (step 2). BGLF4 may further phosphorylate BFRF1 and BFLF2 for their correct localization in the nuclear membrane. Subsequently, the BFRF1/BFLF2 complexes may recruit a cellular kinase(s) such as PKC to facilitate the reorganization of and interaction with the lamina (step 3). Finally, EBV nucleocapsids pass through the barrier of the nuclear lamina and proceed to primary envelopment (step 4). ONM, outer nuclear membrane. ER, endoplasmic reticulum.