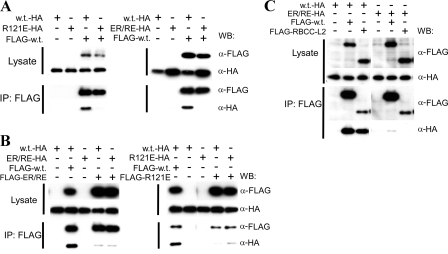
FIG. 3.
Contribution of the B-box 2 domain to higher-order self-association of TRIM5αrh. (A) The coprecipitation of HA-tagged TRIM5αrh variants with FLAG-tagged TRIM5αrh was examined. 293T cells were transfected transiently with pLPCX plasmids expressing C-terminally HA-tagged wild-type (w.t.) TRIM5αrh, R121E, or ER/RE or N-terminally FLAG-tagged wild-type (w.t.) TRIM5αrh. Cytosolic lysates containing the TRIM5αrh variants were prepared, and the concentration of TRIM5 protein in the lysates was adjusted to account for differences in the levels of expression, as described in Materials and Methods. The adjusted lysates were then mixed in a 1:1 ratio and used for precipitation with an anti-FLAG antibody. The amounts of HA- and FLAG-tagged proteins in the lysates and immunoprecipitates (IPs) were analyzed by Western blotting (WB) with HRP-conjugated anti-HA and anti-FLAG antibodies. (B) The ability of TRIM5αrh ER/RE and R121E to associate with themselves in the coimmunoprecipitation assay was examined. The assay was carried out as described above using N-terminally FLAG-tagged TRIM5αrh ER/RE and R121E in addition to the FLAG-tagged wild-type TRIM5αrh protein (FLAG-w.t.). (C) The requirement for the B30.2(SPRY) domain for the higher-order self-association of TRIM5αrh was examined. An N-terminally FLAG-tagged truncation mutant of TRIM5rh (RBCC-L2), which lacks a B30.2(SPRY) domain (16), was used in the coimmunoprecipitation assay along with HA-tagged wild-type TRIM5αrh and TRIM5αrh ER/RE.