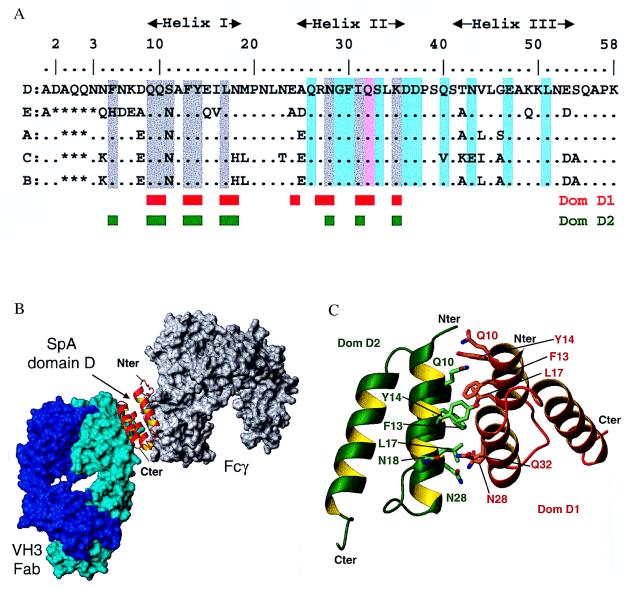
Figure 2.
Interactions of individual SpA domains. (A) Alignment of the amino acid sequences of the five SpA domains. Domain D residues involved in interaction with Fab 2A2 are highlighted in cyan. With the exception of Gln-32 (pink), there is no overlap between the residues involved in Fab interaction and those mediating Fcγ binding (2) (gray highlight). The engineered domain Z differs by the key mutation Gly-29 in Ala and does not bind Fab. The residues involved in the dimer of domain D observed in the asymmetric unit are indicated by red and green boxes. (B) Cross-linking of a VH3 Fab (cyan surface) and a Fcγ (gray surface) by a single domain of SpA (red ribbon). This model is based on the superposition of helix I and II of SpA domains in the Fab-domain D complex reported here and in the previously determined Fcγ-domain B complex (2) (rmsd of 0.73 Å for 140 backbone atoms). (C) Interface between domain D monomers. Schematic view of the interaction between the two domains D observed in the asymmetric unit, dom-D1 (red ribbon) and dom-D2 (green ribbon). Contact residues from both domains are shown in stick representation.