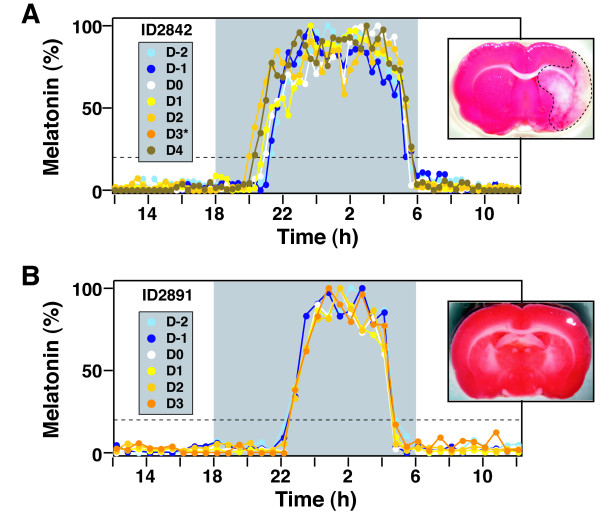
Figure 2.
Effect of MCAo on rhythmic secretion of melatonin. Melatonin secretion was measured in animals before and after surgery. Representative animals undergoing MCAo (A) and sham surgery (B) are shown. Tracings represent daily melatonin profiles superimposed upon the time of the day, with the gray shaded area representing lights off. Each day is demonstrated in a different color. D-2 and D-1 are two and one day before surgery. D0 is the day of the surgery, which was performed in the daytime. Days one to four (D1 to D4) are post-operative days. MCAo caused an advance of MT-on that persisted through four days of monitoring (A). MCAo slightly delayed the MT-off. Due to technical reasons, the data for the third postoperative day was lost (D3*). TTC stained brain sections are displayed to demonstrate that MCAo induces cortical and subcortical infarction. Sham surgery (B) did not affect MT-on or MT-off timing and did not cause brain infarction.