Abstract
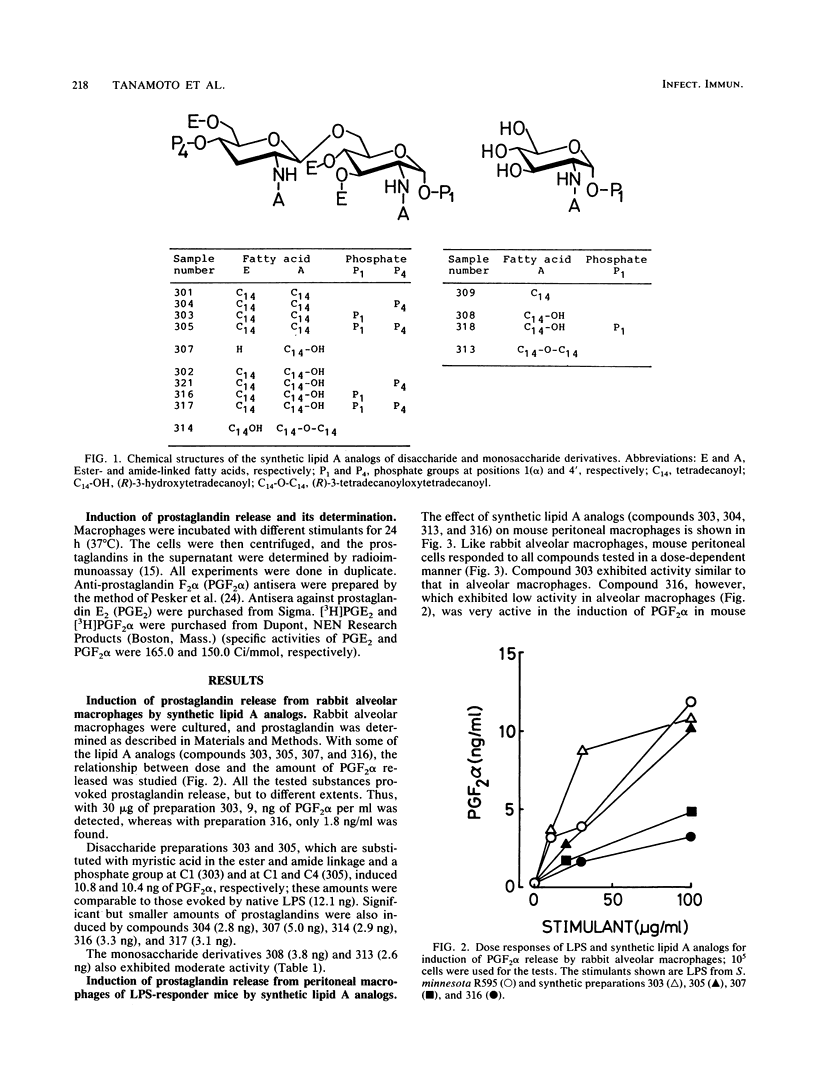
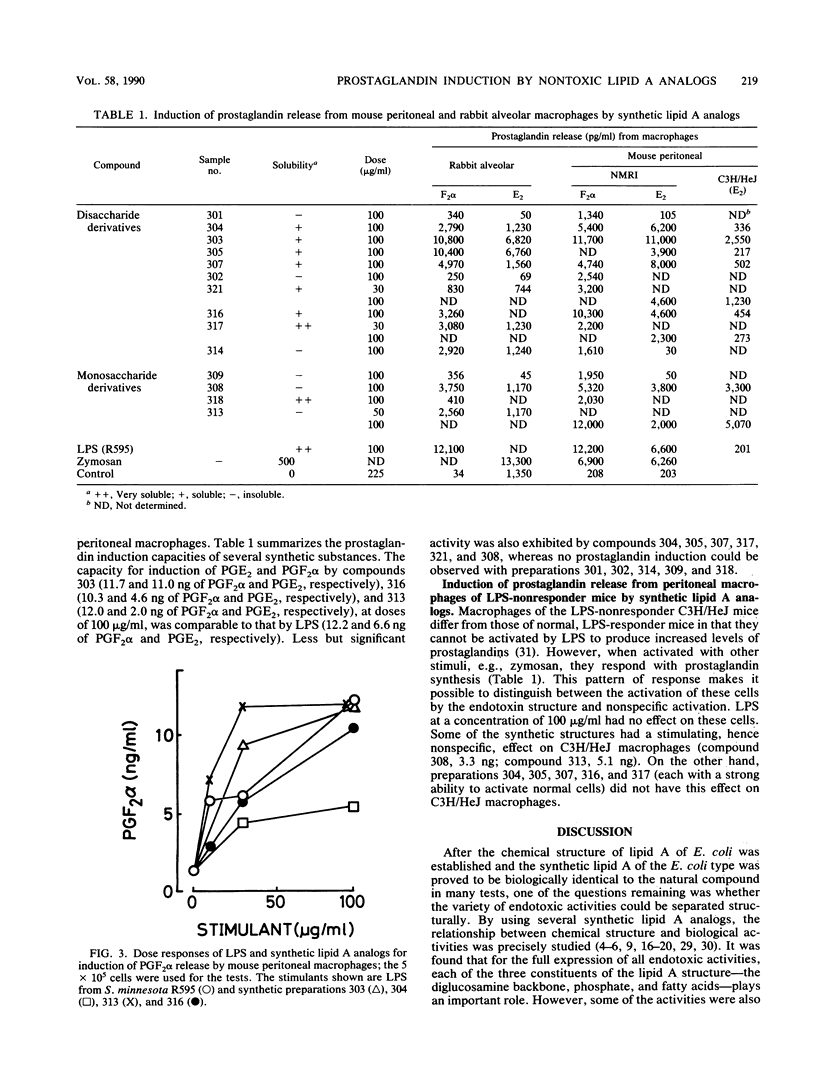
The ability of synthetic lipid A analogs to induce prostaglandin synthesis in macrophages was compared with that of native lipopolysaccharide. The synthetic preparations comprised monomeric or dimeric derivatives of D-glucosamine with different patterns of substitution by phosphate and tetradecanoic, (R)-3-hydroxytetradecanoic, and (R)-3-tetradecanoyloxytetradecanoic acid. All of these preparations are structurally distinct from native lipid A (principally regarding the position of fatty acid substitution) and hence have been previously shown to be endotoxically inactive in many biological tests. It was found that many of these synthetic samples exhibit strong activity in inducing prostaglandin E2 and prostaglandin F2 alpha, with some of them having activity comparable to that of lipopolysaccharide. Experiments with macrophages of C3H/HeJ mice enabled us to differentiate between endotoxin-specific (in the case of dimeric preparations) and endotoxin-nonspecific (for monomeric preparations) mechanisms for the induction of prostaglandins. These results indicate that there is a difference in the mechanism of induction of prostaglandin synthesis between monomeric lipid A's and dimeric or native lipid A structures.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cranston W. I. Central mechanisms of fever. Fed Proc. 1979 Jan;38(1):49–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher J. R., Ramwell P. W. E. coli endotoxin shock in the baboon: treatment with lidocaine or indomethacin. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Res. 1978;3:183–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn J. T. Endotoxic shock in the rabbit: the effects of prostaglandin and arachidonic acid administration. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1978 Sep;206(3):555–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Freudenberg M., Brade L., Schade U., Rietschel E. T., Kusumoto S., Shiba T. Biological activity of synthetic heptaacyl lipid A representing a component of Salmonella minnesota R595 lipid A. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 1;160(1):55–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09939.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Rietschel E. T., Westphal O., Brade H., Brade L., Freudenberg M., Schade U., Imoto M., Yoshimura H. Synthetic and natural Escherichia coli free lipid A express identical endotoxic activities. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Apr 1;148(1):1–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton J. G., Wells C. H. Effects of indomethacin and nicotinic acid on E. coli endotoxin shock in anesthetized dogs. J Trauma. 1976 Dec;16(12):968–973. doi: 10.1097/00005373-197612000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma J. Y., Matsuura M., Kanegasaki S., Kawakubo Y., Kojima Y., Shibukawa N., Kumazawa Y., Yamamoto A., Tanamoto K., Yasuda T. Structural requirements of lipid A responsible for the functions: a study with chemically synthesized lipid A and its analogues. J Biochem. 1985 Aug;98(2):395–406. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobke A., Peskar B. A., Peskar B. M. On the specificity of antisera against prostaglandins A2 and E2. FEBS Lett. 1973 Dec 1;37(2):192–196. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80456-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanegasaki S., Kojima Y., Matsuura M., Homma J. Y., Yamamoto A., Kumazawa Y., Tanamoto K., Yasuda T., Tsumita T., Imoto M. Biological activities of analogues of lipid A based chemically on the revised structural model. Comparison of mediator-inducing, immunomodulating and endotoxic activities. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Sep 3;143(2):237–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08364.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanegasaki S., Tanamoto K., Yasuda T., Homma J. Y., Matsuura M., Nakatsuka M., Kumazawa Y., Yamamoto A., Shiba T., Kusumoto S. Structure-activity relationship of lipid A: comparison of biological activities of natural and synthetic lipid A's with different fatty acid compositions. J Biochem. 1986 Apr;99(4):1203–1210. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotani S., Takada H., Takahashi I., Tsujimoto M., Ogawa T., Ikeda T., Harada K., Okamura H., Tamura T., Tanaka S. Low endotoxic activities of synthetic Salmonella-type lipid A with an additional acyloxyacyl group on the 2-amino group of beta (1-6) glucosamine disaccharide 1,4'-bisphosphate. Infect Immun. 1986 Jun;52(3):872–884. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.3.872-884.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotani S., Takada H., Tsujimoto M., Ogawa T., Harada K., Mori Y., Kawasaki A., Tanaka A., Nagao S., Tanaka S. Immunobiologically active lipid A analogs synthesized according to a revised structural model of natural lipid A. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):293–296. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.293-296.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotani S., Takada H., Tsujimoto M., Ogawa T., Takahashi I., Ikeda T., Otsuka K., Shimauchi H., Kasai N., Mashimo J. Synthetic lipid A with endotoxic and related biological activities comparable to those of a natural lipid A from an Escherichia coli re-mutant. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):225–237. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.225-237.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurland J. I., Bockman R. Prostaglandin E production by human blood monocytes and mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):952–957. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegert R., Philipp-Dormston W. K., Radsak K., Menzel H. Mechanism of fever induction in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1976 Nov;14(5):1130–1137. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.5.1130-1137.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarnes R. C., Harper M. J. Relationship between endotoxin-induced abortion and the synthesis of prostaglandin F. Prostaglandins. 1972 Mar;1(3):191–203. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(72)90004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanamoto K., Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Kusumoto S., Shiba T. Mitogenic activities of synthetic lipid A analogs and suppression of mitogenicity of lipid A. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):427–433. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.427-433.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanamoto K., Zähringer U., McKenzie G. R., Galanos C., Rietschel E. T., Lüderitz O., Kusumoto S., Shiba T. Biological activities of synthetic lipid A analogs: pyrogenicity, lethal toxicity, anticomplement activity, and induction of gelation of Limulus amoebocyte lysate. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):421–426. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.421-426.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl L. M., Rosenstreich D. L., Glode L. M., Sandberg A. L., Mergenhagen S. E. Defective prostaglandin synthesis by C3H/HeJ mouse macrophages stimulated with endotoxin preparations. Infect Immun. 1979 Jan;23(1):8–13. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.1.8-13.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


