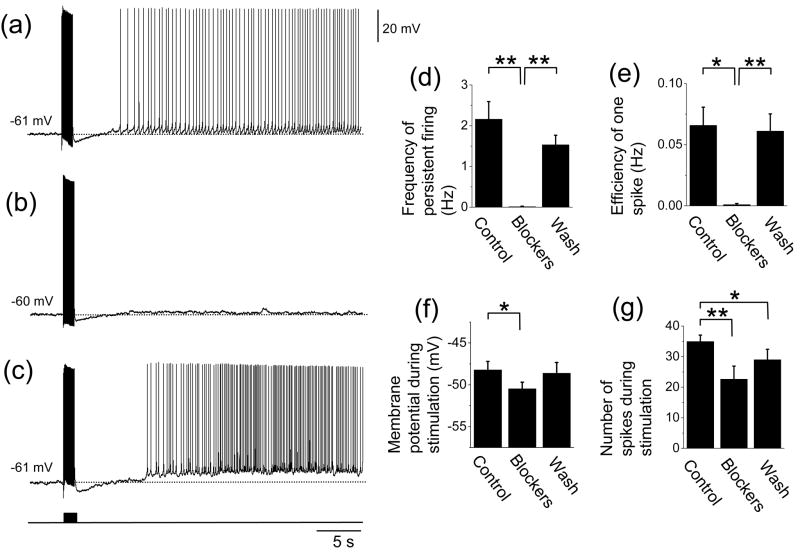
Fig. 3.
Effect of mGluR blockers on persistent firing induced by synaptic stimulation. (a) – (c) Persistent activity in a representative cell in (a) control (with atropine, ionotropic glutamate synaptic blockers and GABAergic synaptic blockers), (b) group I mGluR blockers and (c) after wash out of the group I mGluR blockers. (d) Frequency of persistent firing. (e) Efficiency of one spike to cause persistent firing. (f) Membrane potential during stimulation. (g) Number of spikes during stimulation. Note significant decrease in the frequency of persistent firing and the efficiency of one spike. Significances from Tukey post-hoc test are shown. *: 0.01 ≤ P < 0.05, **: 0.001 ≤ P < 0.01, ***: P < 0.001. Differences between pairs without asterisks were not significant.