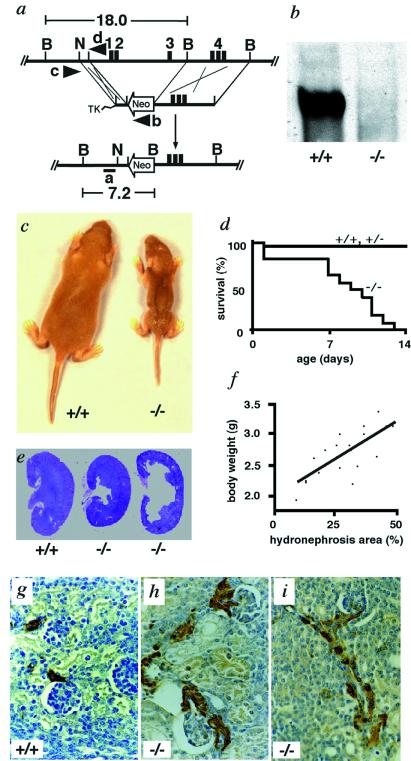
Figure 1.
Targeted inactivation of the NKCC2 gene and analysis of NKCC2−/− pups. (a) Gene targeting strategy. (Top) The region of the NKCC2 gene extending from the promoter to intron 4. (Exon 4 has three parts, 4B, 4A, and 4F.) (Middle) Targeting construct. (Bottom) Targeted allele in which the gene is disrupted and 12 kb from 2.5 kb upstream of transcription initiation site to part of intron 3 is replaced with the neomycin resistance gene, Neo. TK, Herpes simplex virus-thymidine kinase gene. 1–4 are exons 1–4. Restriction sites are B, BamHI; N, NheI. The positions of probe a and primers b–d are indicated. (b) Western blot analysis of kidney homogenate from +/+ and −/− mice. The blot was exposed to anti-NKCC2 antibody. (c) Growth retardation and poor turgor of −/− mice. Wild-type (+/+) (Left) and homozygous mutant mouse (−/−) (Right) from the same litter at 7 days after birth. (d) Mortality rate of −/− mice and control mice, +/+ and +/−. Dead animals were collected daily and genotyped. +/+, n = 15; +/−, n = 25; −/−, n = 13. (e) Kidneys from +/+ and −/− mice at 7 days of age stained with hematoxylin and eosin. (Original magnification: ×1.) (f) Correlation between severity of hydronephrosis and body weight of 7-day-old −/− pups. n = 19, correlation coefficient 0.7269, R2 = 0.528, P < 0.0001. (g–i) Renin immunohistochemistry with kidney sections from 7-day-old pups. (g) Renin staining (brown) is confined to the afferent arterioles in +/+. (h and i) Renin staining includes afferent arterioles and extends along them in the direction of the interlobular arteries. Efferent arterioles and glomeruli are also renin positive. (Original magnification: ×200.)