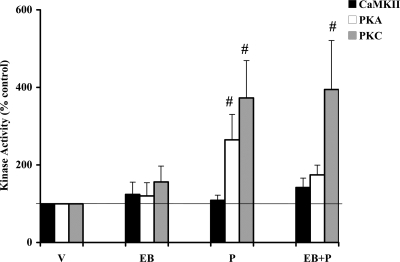
Figure 5.
P regulation of PKA and PKC basal activities remained unaltered by CaMKII inhibitor KN-93 in the VMN. VMN tissue sample homogenates from the treatments groups administered KN-93 in Fig. 4 were processed for kinase assays as described in Materials and Methods. The homogenates were assayed for basal PKA, PKC, and CaMKII activities. The CaMKII activity was normalized to the vehicle (V) in the presence of KN-93 and expressed as percentage of the respective control (mean ± sem; 100%). ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post hoc multiple comparisons demonstrated significant differences between P-stimulated PKA (#, P < 0.05) and PKC (#, P < 0.05) basal activities, compared with the vehicle control, in the presence of KN-93. Significant difference in the PKC basal activity was also observed between EB+P and vehicle control (#, P < 0.05) in the presence of KN-93 (n = 6 in each treatment group).