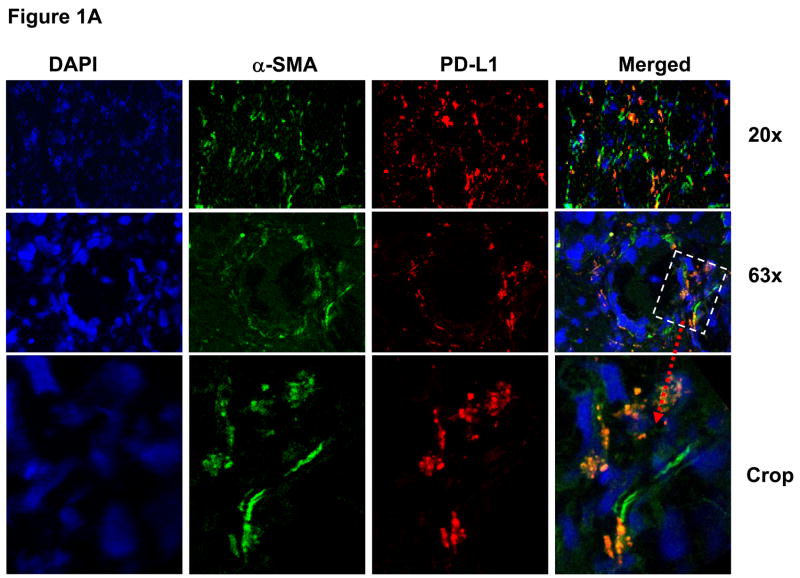
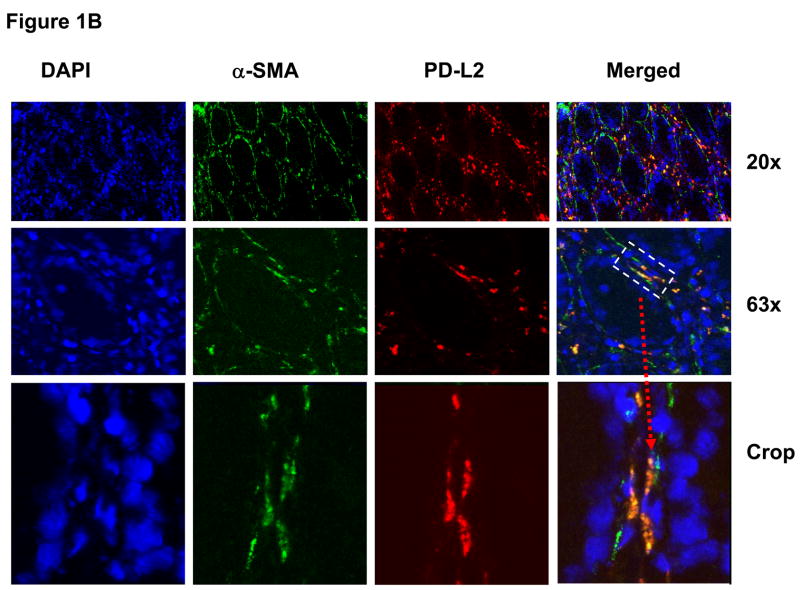
Figure 1.
Normal human colonic myofibroblasts express (A) PD-L1 and (B) PD-L2 molecules in situ. The panels show confocal microscopy analysis of multicolor immunofluorescent staining of a representative frozen tissue cross sections of a normal colonic crypt fixed in 2% paraformaldehyde. The myofibroblast cell population was identified in colonic mucosa based on morphology, subepithelial location and positive immunoreactivity for α-SMA. Cell nuclei (in blue) were stained with DAPI. Subepithelial pericryptal myofibroblasts were identified by expression of α-SMA (in green) as detected by AF® 488 conjugated anti-human α-SMA murine mAbs (clone 1A4). PD-L1 or PD-L2 staining (in red) of colonic mucosa was performed using AF® 647 or AF® 546 labeled (A) anti-PD-L1 murine mAbs (clone M1H1) or (B) anti-PD-L2 murine mAbs (clone M1H18). Merged images clearly demonstrate expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2 on α-SMA+ cells (e.g. myofibroblasts, in orange-yellow staining).