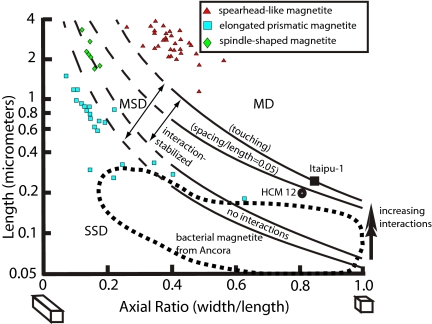
Fig. 5.
Domain-stability diagram of the upper limit for SD magnetization calculated from micromagnetic models of prismatic magnetite crystals (39). Interaction effects and chain arrangements increase this upper size limit, and shape anisotropy stabilizes SD behavior for any given maximum crystal size. The largest magnetosome crystals yet observed from living bacteria are indicated: the largest cuboidal particles from strain Itaipu-1 (40) and the largest hexaoctahedral prisms and bullet particles from the Ammersee and Moorsee, respectively (9). The large, unusual PETM magnetofossils of elongate hexaoctahedral and spindle-like morphologies are mostly stable single domain (SSD) or metastable single domain (MSD). We hypothesize that unusual crystal-tip truncations of these forms impede development of the metastable flower-like structure magnetization. Spearhead-like magnetite crystals are of a size that should be multidomain, attesting to the likelihood of their nonmagnetotactic biological function. Other considerations suggest that these crystal forms may have been used for protection by iron-biomineralizing eukaryotes.