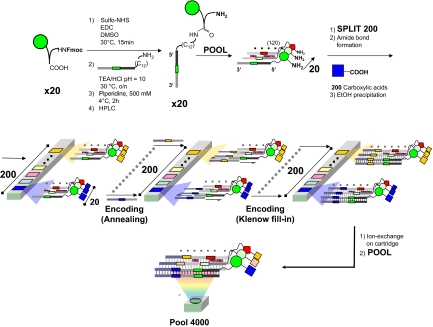
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of the strategy used for the synthesis and encoding of the DEL4000 library. Initially, 20 different Fmoc-protected amino acids were coupled to unique oligonucleotides derivatives, carrying a primary amino group at the 5′ extremity. Subsequently, these derivatives were pooled and coupled to 200 carboxylic acids in parallel reactions. The identity of each carboxylic acid was encoded by means of a Klenow polymerization step, by using a set of partially complementary oligonucleotides. This procedure resulted in a 4,000-member library (DEL4000), in which each chemical compound was covalently attached to a double-stranded DNA fragment, containing 2 coding domains that unambiguously identify the compound's structure (i.e., the 2 chemical moieties used for compound synthesis).